America’s Biggest AI Safety Concerns (Study)
For many years, some have argued that, if misused, artificial intelligence could have a negative impact on the future of humanity. For a long time, many people either had no idea about these concerns or put them on the back burner as the prospect of AI impacting our day-to-day’s appeared to be decades away.
However, we have seen this altering during the past few years. We’ve witnessed significant advancements in the capabilities of AI systems, and a recent survey from HigherVisibility indicates that many people are worried about what the progression in AI systems will mean for them; whether it will impact their work, education, all the way down to their basic human rights.
It’s no secret that some individuals are becoming more fearful as artificial intelligence advances and develops. With this in mind, HigherVisibility has surveyed the US public to gain an understanding of what the highest concerns are when it comes to the development of AI in today’s society.
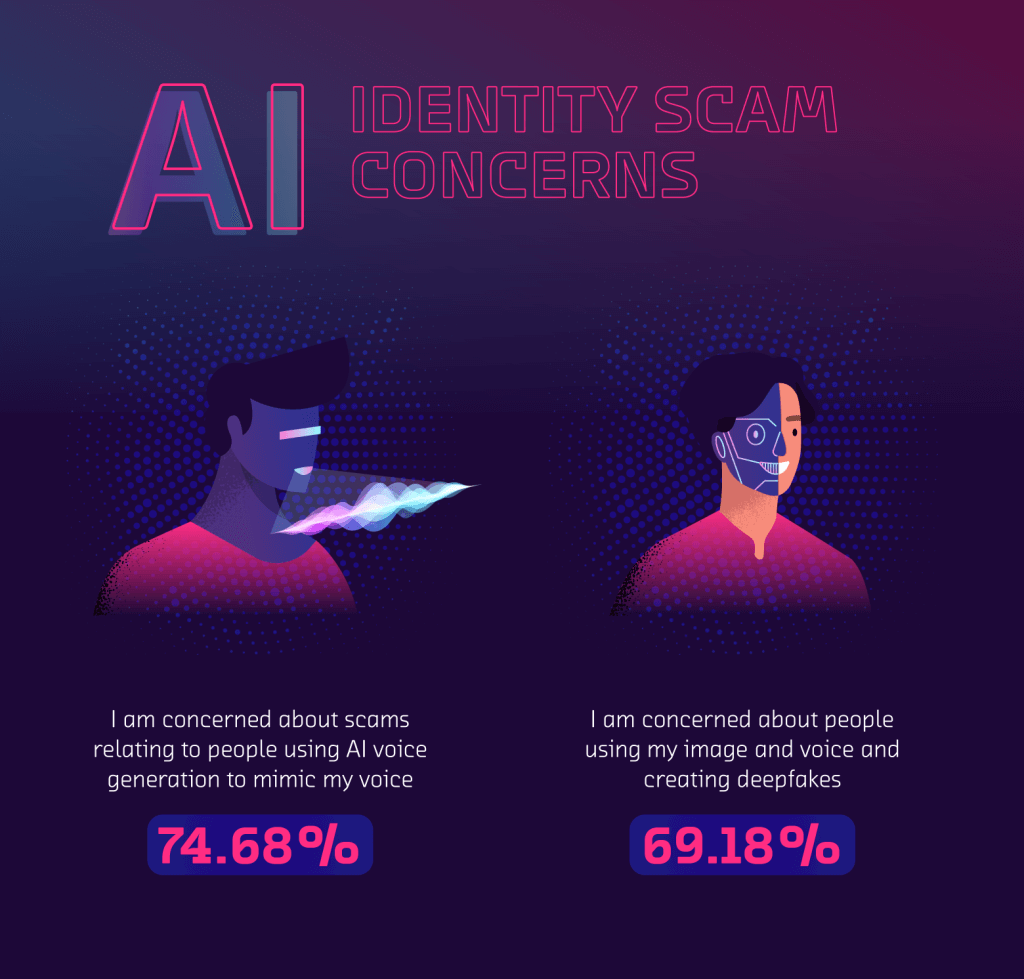
The study found that when it came to AI concerns, scam concerns were among the most predominant. Over 7 in 10 people (74.68%) in the US are concerned about scams relating to people using AI voice generation in order to mimic their voices. Voice cloning is a technique used in which a scam artist is able to locate an audio clip of a person’s voice and submit this to a tool that aims to imitate an individual’s voice. In fact, a study by McAfee found that it takes just “3 seconds of audio to produce an 85 percent match to a person’s voice”.
Interestingly, the generation most concerned with voice scams were Millenials, with almost 4 in 5 (79.29%) worried about their voices being used in a scam. They were closely followed by Baby Boomers (78.41%), whilst Gen Z (62.54%) were the least troubled.
While there isn’t a huge amount of information detailing the prevalence of AI scam calls, instances have been reported by TikTok users over the past couple of years, raising concerns about the danger that AI poses. Our study also found that over 3 in 5 people (69.18%) are concerned about scam artists using their images and voices to create deepfakes.
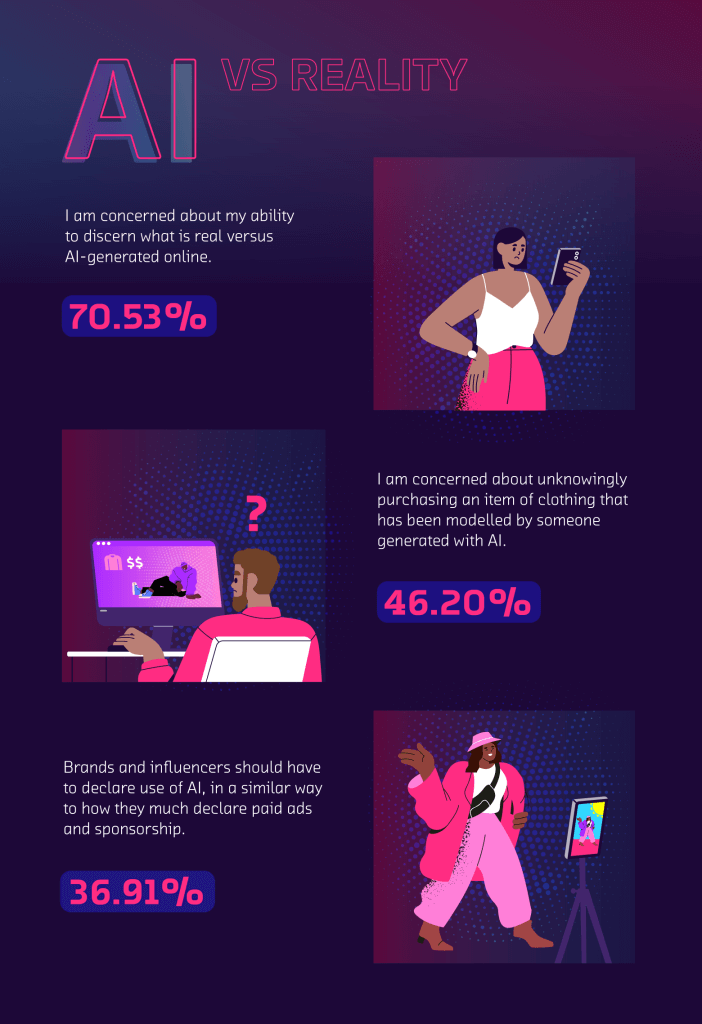
The study also looked at how AI is impacting our view of reality, with a shocking statistic revealing that over 70% of Americans are now concerned about their abilities to discern what is real online and what is AI-generated. Additionally, nearly 1 in 2 people (46.20%) are concerned about unknowingly purchasing an item of clothing online which has been modeled by someone generated by AI. This was a predominant fear in men, of which 54.73% agreed, in comparison to 37.98% of women.
Influencer culture is a phenomenon that we have witnessed evolve over the years, but now, with the increasing accessibility of AI programs and rising fears of being unable to discern between AI and reality, almost 2 in 5 people (36.91%) believe that brands and influencers should now have to declare the use of AI in their materials, in a similar way to influencers being required to highlight paid ads and sponsorship deals.
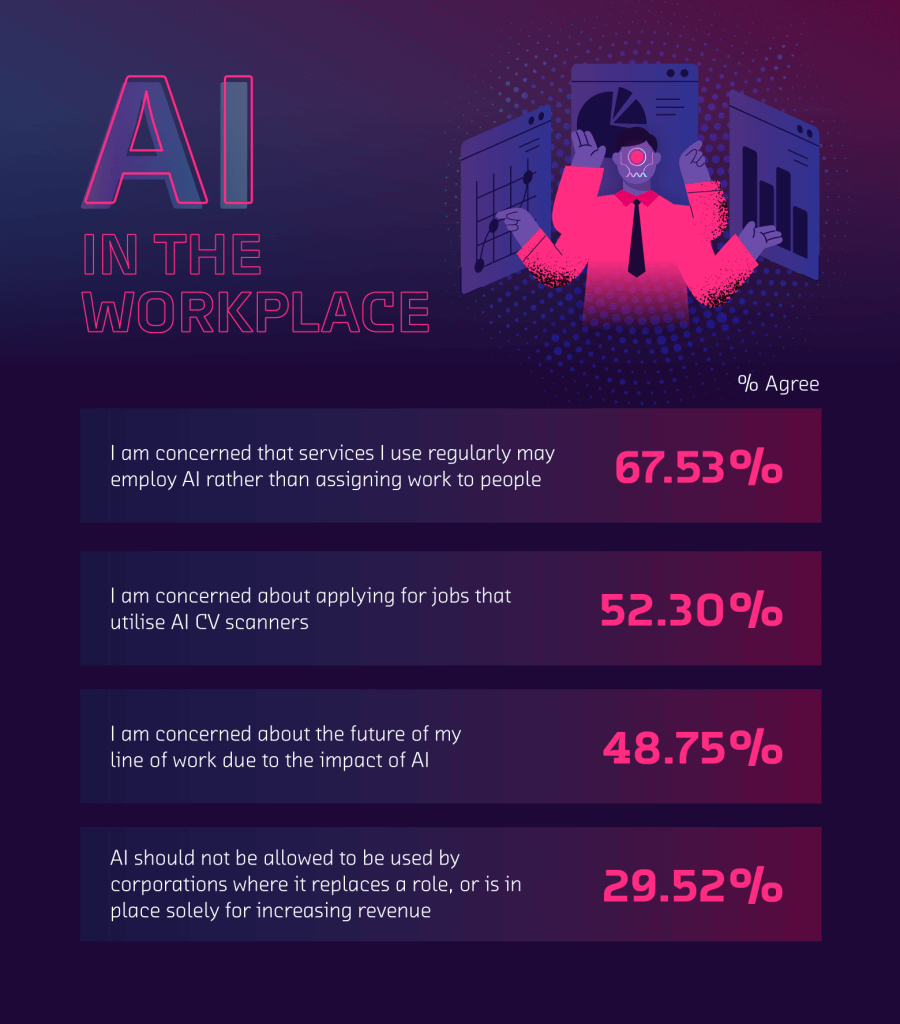
One of the most prominent discussions surrounding the use of AI in today’s society is the implementation of AI within the workplace. The search term for ‘will AI take over my job’ has seen a 69% rise on Google over the past year, alongside countless articles detailing the abilities of AI and the jobs that could be at risk due to these developments.
In fact, a study from March 2023 by Goldman Sachs even predicted that AI would be able to replace “the equivalent of 300 million full-time roles” throughout Europe and the US, claiming that automation may “eventually take over ¼ of work tasks.”
Our study found that almost 1 in 2 people in the US (48.75%) are concerned about the future of their line of work due to the impact of AI, with over 1 in 4 (29.52%) agreeing that AI shouldn’t be allowed to be used by corporations where it replaces a role or is in place solely for increasing revenue.
In many aspects, the exponential growth of AI has been compared to the growth of social media, where concerns about regulation and countering false information are rampant.
Citizens frequently believe that their consumer rights have not been upheld when it comes to social media platforms, and due to legislation only being put into place 25 years ago, there are many who believe that there is reason to be concerned about security and privacy when it comes to AI programs.
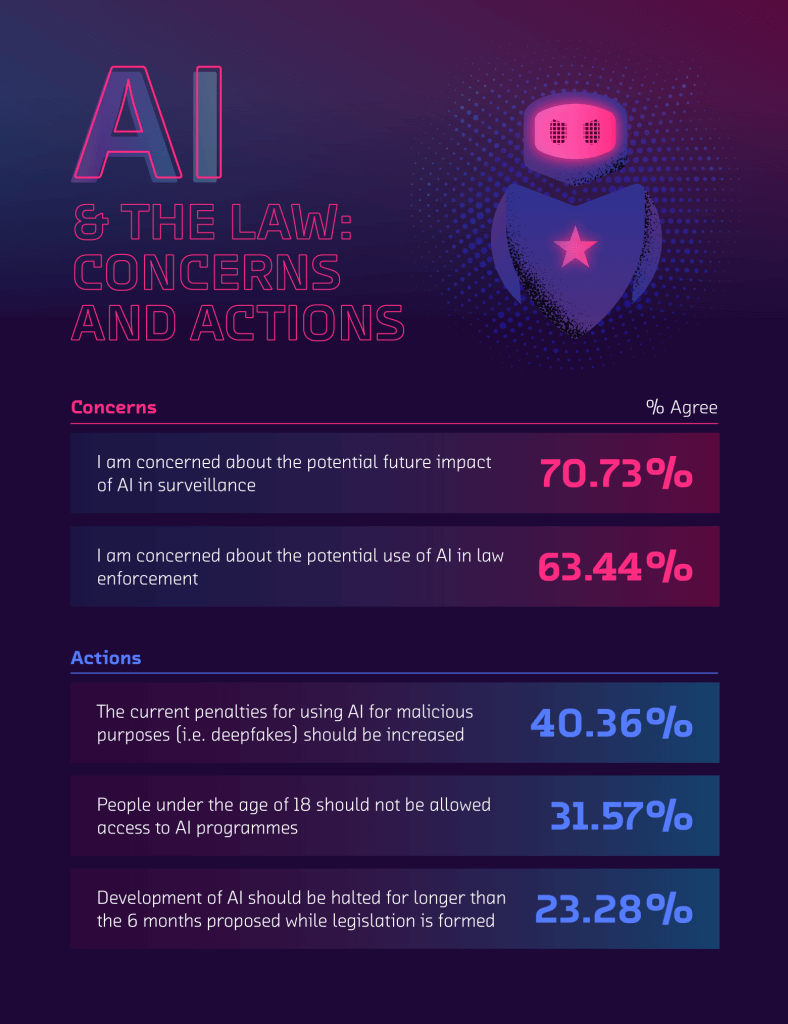
Whilst there is a lot of potential for technical advancements within AI to be used in a positive way, there also lies the possibility that the technology could be abused. As such, 2 in 5 people (40.36%) believe that the current penalties for using AI for malicious purposes (i.e., deep fakes) should be increased. A further 31.57% of people also believe that people under the age of 18 should not be allowed to access AI programs.
A huge concern of the US public is the potential future impact of AI in surveillance, with 7 in 10 people (70.73%) concerned about those in power utilizing the technology to move beyond protecting people’s safety to unregulated monitoring and a clear violation of human rights and privacy. In addition to this, OECD data found that just 31% of US citizens trust and have confidence in their government, potentially giving reason as to why citizens are hesitant to extend the power that others have over them.
Joe Biden and Kamala Harris met with chief executives in May 2023 in order to put measures in place to address concerns the public has in regard to the fast development of AI. In a statement, the government claimed companies creating the technology had a “fundamental responsibility to make sure their products are safe before they are deployed or made public”, and have put in place plans to invest in new AI research institutes to seek AI advancements that are “ethical, trustworthy, responsible, and serve the public good”.
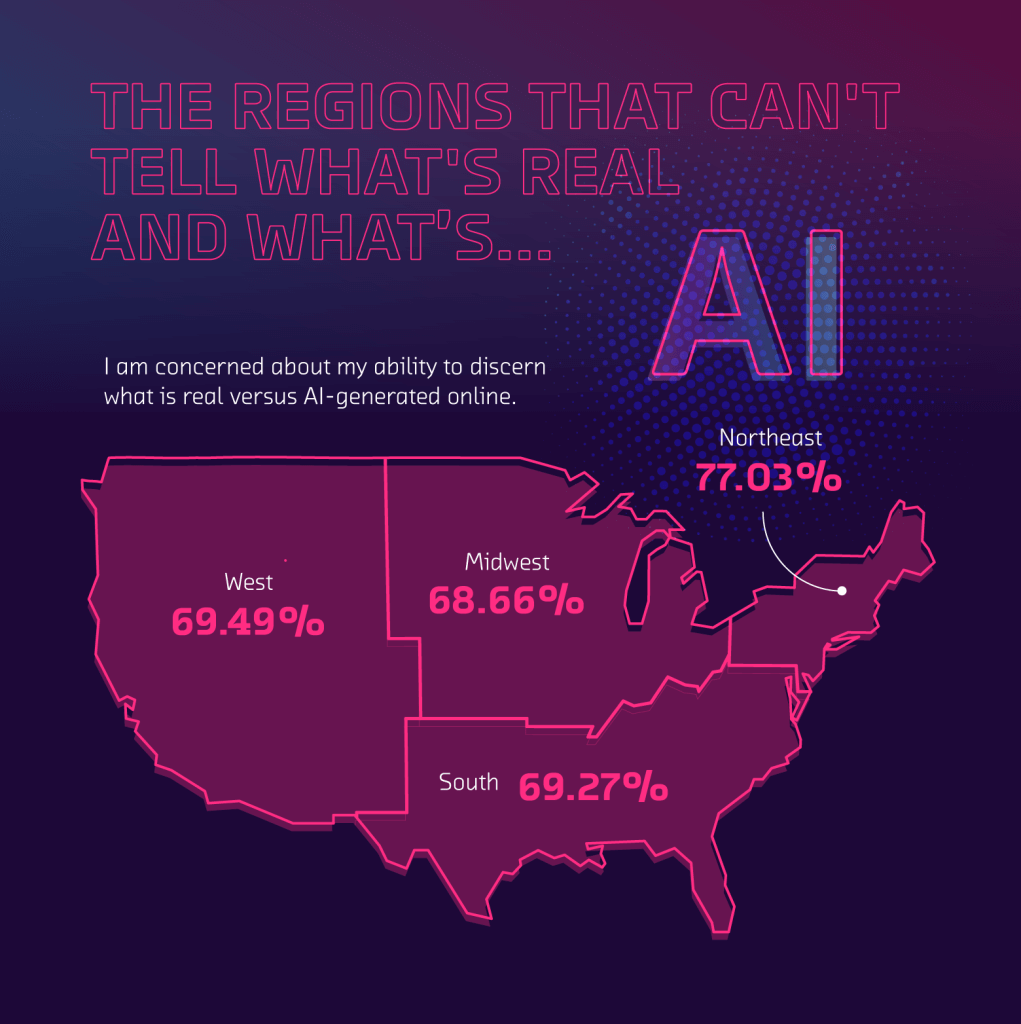
Taking a look at the regions finding the most difficulty in discerning between AI and reality, the study found that an alarming 77.03% of people in the Northeast are concerned about being able to identify which is which. This was followed closely behind by the West (69.49%), South (69.27%), and Midwest (68.66%).
The cities finding it the hardest to identify what is real and what is AI are New York (83.66%), Texas (75.40%), and Illinois (72.84%).
The narrative of AI within the United States is still very much in its infancy; however, given the popularity of tools such as ChatGPT and DALL-E, awareness of AI among the public is continuing to grow. As its influence increases, will US citizens begin to welcome the more apparent implementation of AI in their everyday lives and political systems, or will fear of the technology continue to create hesitance of acceptance in the future?
———————————–
Methodology
The research was conducted using Censuswide with 2,002 general consumers (nat rep) in the USA between 19.05.23 – 22.05.23. Censuswide abides by and employs members of the Market Research Society, which are based on the ESOMAR principles.
