SEO Performance Tracking: Tips to Measure and Improve SEO
Every activity towards SEO is to improve your site’s visibility and attract relevant visitors. But the best way to know if your SEO efforts are achieving any tangible results is by tracking your performance.
SEO performance measures how well your website ranks in search engines like Google. While optimizing your site for organic traffic takes time, it’s important to know what’s working and what needs improvement in the meantime.
To do that, Google recommends checking;
- The number of times a user saw your site or page in search results (impressions).
- The number of times someone clicked a link to your site from Google’s SERP (click-through rate).
- The average position of your site on SERPs (average position).
- The user’s search intent when your page came up (query).
In this article, I’ll explore these performance metrics, and discuss more to measure and improve your SEO performance.
8 KPIs for SEO Performance Tracking: Measure Your Success
These are eight ways you can measure your website’s SEO success. To effectively measure SEO performance, it is essential to track various metrics and understand key performance indicators (KPIs). Additionally, conducting thorough keyword research is crucial for identifying what prospects care about and uncovering underutilized keywords, which can significantly enhance your online presence and drive organic search traffic.
1. Organic Traffic
Organic search traffic refers to the users who visit your website through unpaid search results.
It is the traffic you get when people type in a query on search engines, see your site, and click through to your page. The ultimate goal of SEO is to increase this kind of traffic— so this should be your first indicator.
To track your organic traffic over the past few months, log in to Google Analytics.
- Go to Audience, and click on Overview.
- Click on the Add Segment option at the top of the page,
- It will bring a list of segmented names. Click on organic traffic.
- You can set a duration for the past few months to see how well your site has performed during that time.
If your organic traffic is increasing, you’re on the right track.
But if you see stagnant or declining numbers, it’s a sign that your SEO strategy may need adjustments.
While SEO does take time to show results, you should see some improvement within 2-3 months of consistent effort.
You can also use tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs. Here’s an example from SEMrush:
Navigate to domain overview and enter your website URL:
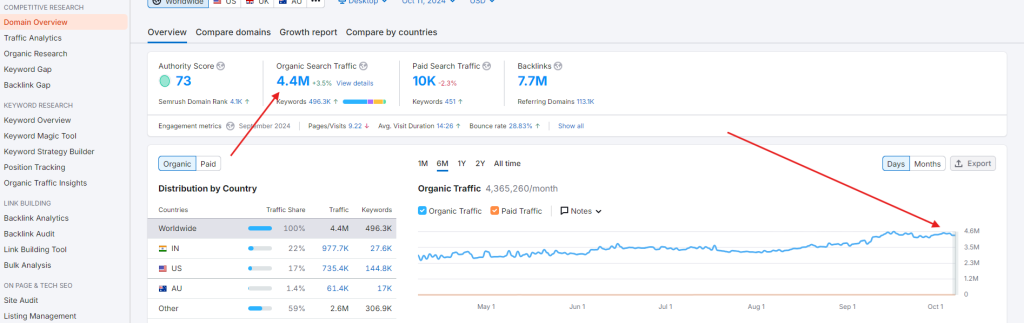
If you’ve been working hard on SEO but your traffic remains low, it could be because:
- You have outdated content on your website
Your content won’t rank well or attract visitors if it’s outdated. Readers will choose a webpage with content published in 2024 over one that’s published in 2019. Update and refresh your content with new information and statistics; you can also optimize your pages for newer keywords so they are more visible to users searching for those queries.
- You’re not using the People Also Ask and FAQs sections
Find common questions that people ask relating to your topic, and answer them directly in your content. This will increase your chances of appearing on the Information Hub, which will boost your visibility. See example:
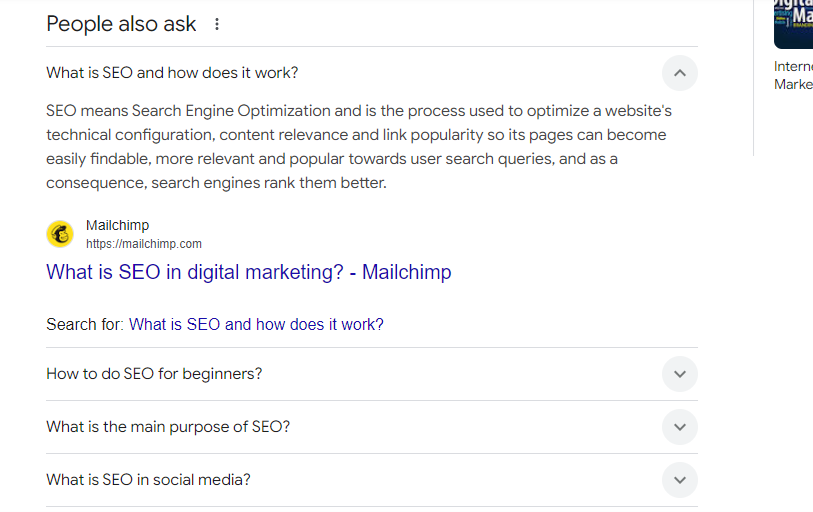
- You’re not publishing content regularly.
Consistency is key in SEO. Publishing high-quality content regularly shows search engines that your site is active and relevant and can be shown to users.
2. Traffic Sources
Users can visit your site in many ways, and how they do so usually influences their buying decisions.
If your goal is to attract customers who will convert into leads, it’s important to know the different traffic sources that can bring them to your site. Additionally, tracking rankings on search engine results pages is crucial for enhancing organic traffic and assessing overall SERP visibility.
Most traffic sources come from:
- Organic traffic
Organic traffic is visitors who come to your website through unpaid search results. With organic traffic, users search for specific keywords that your website is optimized for and click on non-sponsored results on their SERP.
- Direct Traffic
Direct traffic refers to visitors who search for your website directly from their browser. In this case, users already know your company or brand and are deliberately visiting it.
According to HubSpot, This kind of traffic has a high conversion rate because users already decided to visit and follow through on your CTA if they are impressed.
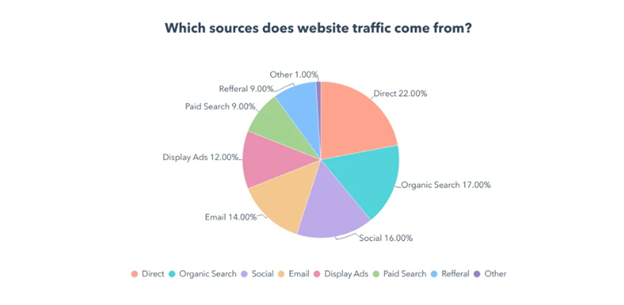
- Referral Traffic
Users may find links to your website on other websites (blogs, online directories, or forums like Reddit).
Referral trafficks are users who click on your link because trusted sources refer you.
You can get more referral traffic if you build relationships with industry influencers, contribute guest posts to authoritative sites, and get your site listed on reputable directories.
- Paid Media
Any user who visits your page through paid ads is paid traffic.
Paid ads are immediate, which means that you’re targeting users looking for your services. When they find your page, they’re usually ready to purchase your services or take another specific action.
This type of traffic is expensive, and you must set your campaigns well to see returns on ad spend.
Others include:
- Social traffic from users who visit your website through social media platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter.
- Email Marketing from users who read your newsletter or click on your promotional campaign on your website.
- Organic video
- Organic shopping
To view your site’s traffic sources in GA4, follow these steps:
- Click “Reports” in the sidebar
- Go to “Acquisition”
- Select “Traffic acquisition”
- Select your date range
Here, you’ll see two charts showing traffic trends from each channel group within your specified timeframe.
Scroll down the report to the table for a complete breakdown of traffic metrics for each channel group.
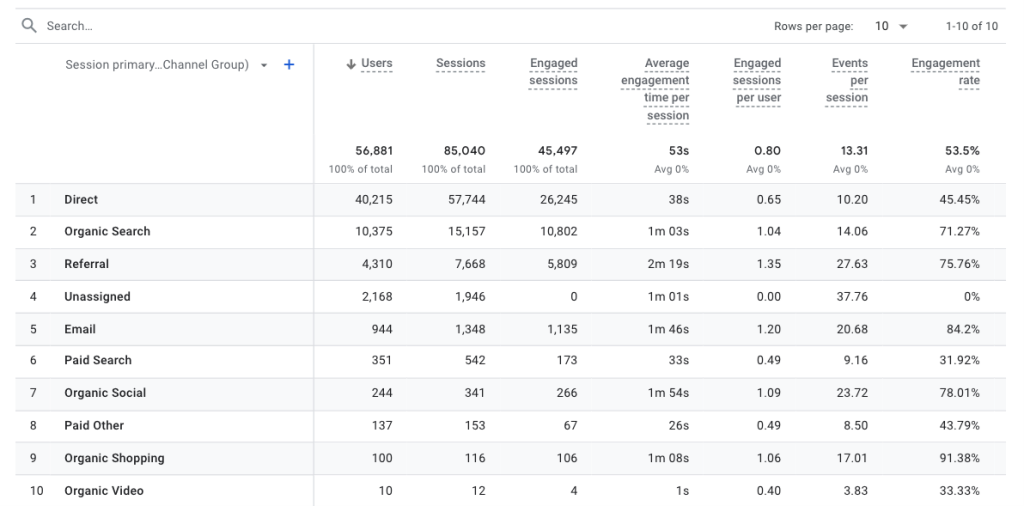
Next, open the drop-down menu at the top-left of the table. Then select “Session source / medium.”
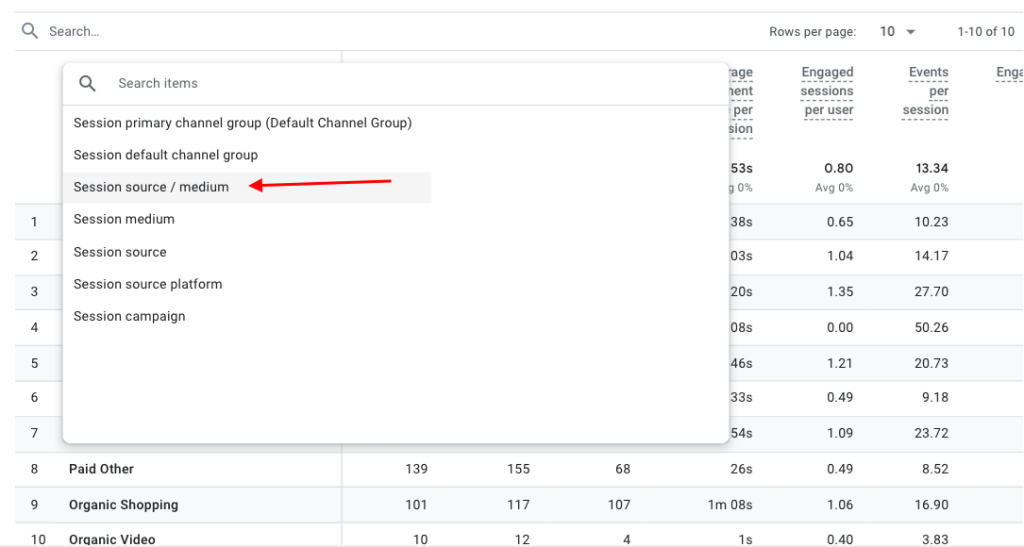
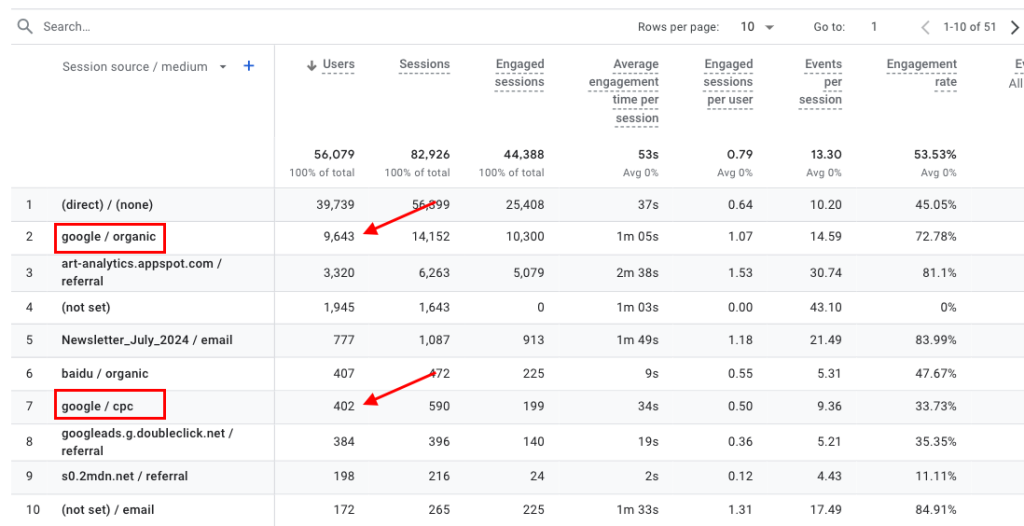
The table will then display where your traffic comes from based on source (e.g. “google”) and medium (e.g. “organic”).
So, in this example, we can see that the site received 9,643 unique visitors from organic Google Search results.
It also received 402 visitors from Google paid search (“cpc”) ads.
Tip: Read more on how to check Google website traffic through Google Analytics 4 here.
3. Keywords Ranking
When you want to rank for a certain keyword, you optimize your content with that keyword to improve your keyword rankings.
This means including it in your titles, headings, and blog posts so that your page pops up when users search for related words to that keyword.
Keyword ranking is your website’s position on a search engine results page (SERP) for a specific keyword or phrase.
Analysis from Backlinko showed that the #1 ranked page in Google’s organic search has an average CTR of 27.6%— that’s over 80m clicks compared to a page on #10.
The report also shows that a page in #1 is 10 times more likely to receive a click than a page in #10.
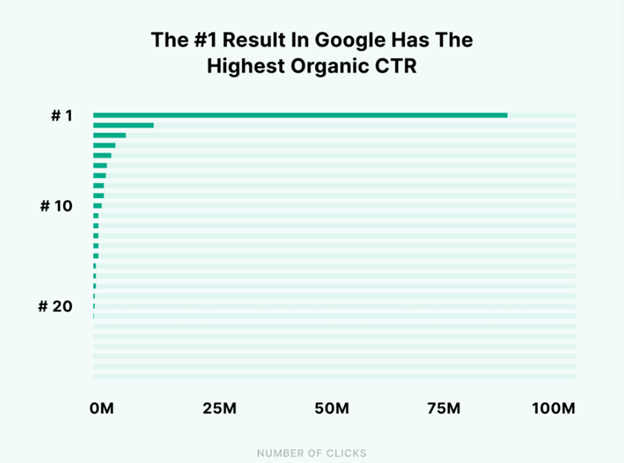
Now, if you ranked #10 on Google’s SERP, for instance, and you doubled your SEO efforts to bring your page to #8. Backlinko says there is no difference.
But this doesn’t mean your efforts are wasted. The SEO strategies that brought you from #10 to #8 can take you to #3 or even #1.
Pro Tip: If an SEO strategy worked but didn’t get you to your goal, continue to implement that strategy, and you will reach that goal.
While a user can see your rankings by searching for a particular keyword, manually monitoring your keyword position on SERPs is difficult.
Instead, use tools like Google Search Console to see what keywords are driving organic traffic to your website. You can also see how your rankings compare to those of your competitors and how you can improve them with GSC.
Here’s a walkthrough Loom video that can help:
Tip: Use the HigherVisibility Rank Checker to know how your website stands out.
4. Bounce Rate
Your website’s bounce rate is the amount of visitors who visit your site and leave without viewing any other page.
A high bounce rate could mean that;
- Your page takes too long to load.
- Users did not understand your website’s layout, which could confuse or discourage them from their next actions.
- They didn’t find what they were looking for.
- They found it, but the content on the page didn’t meet their needs.
According to Backlinko, the amount of time users spend on your site can affect your site ranking.
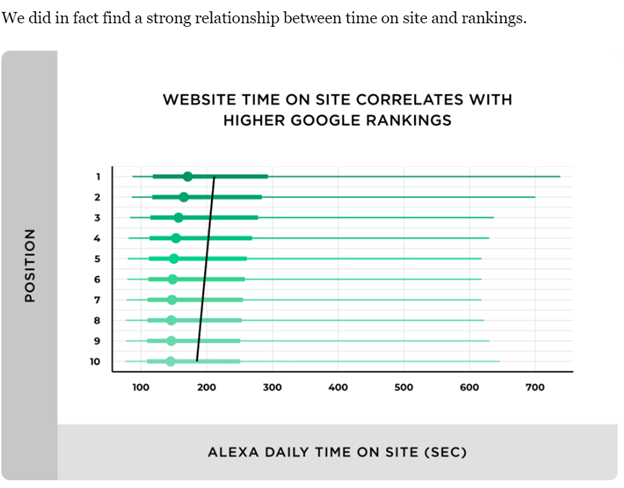
While there is no strong, irrefutable evidence to back this up—even Google denied using time on site as a ranking factor—it has a slight influence on SEO performance.
SEO experts believe that this could mean that the page doesn’t provide what the user is looking for.
But high bounce rates don’t always mean your content isn’t helpful.
It could be that you have mismatched keywords that attract people with search intent you’re not optimized for.
Also, a high bounce rate is typical on informational websites because users come for the information they need and leave when they have it. But most companies optimizing their pages for SEO are probably looking to sell, and this could be a problem.
To track your bounce rate, read Google’s simple guide on GA4.
5. Time On Page
Search intent is important in SEO.
You need to know what your audience is looking for and optimize your content to match their query.
This way, when search engines are delivering relevant results, your page will be at the top.
But what happens when users find your page but cannot stay? You risk not being able to convert them into customers.
This is why time on the page is important. Tracking SEO metrics like time on page is essential for evaluating SEO performance and aligning them with business outcomes.
When a user enters a keyword into Google, clicks on your page, and stays for an extended period, it means that your website content meets their needs or provides value.
On the other hand, if they don’t, it means that your page doesn’t align with their expectations.
You can track your users’ time on your page with Google Analytics.
Log into Google Analytics. Navigate to Reports — Engagement — Pages and Screens.
Under “Average Engagement Time,” there’s a list that shows the average amount of time users spend on each of your pages.
The average time on site for a Google first page result, according to Backlinko, is 2.5 minutes.
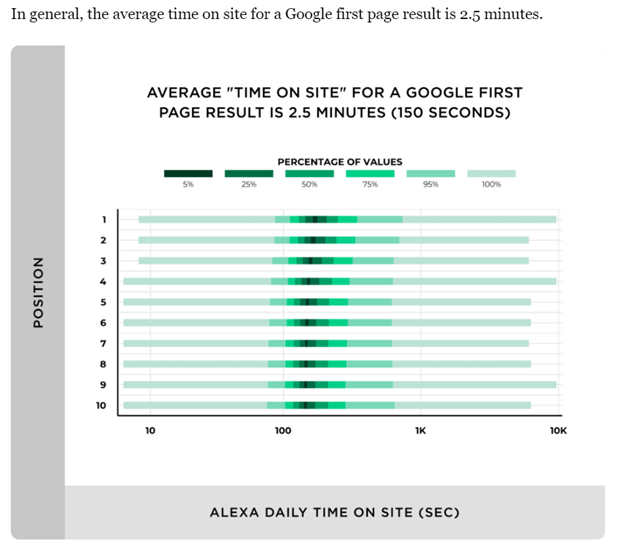
If your time-on-page seems low, you should:
- Create more relevant content. Follow Google’s E-E-A-T when creating your content (more on that later).
- Make your content scannable. Users mostly scan through content, so divide it into pieces with headings, bullet points, and images to make it readable.
- Improve your site structure.
- Link to other pages on your site to help users find related content easily.
6. Conversion
Conversions are actions that users from the search engines take on your website.
They could:
- Sign up for a trial
- Request a free proposal
- Make a call
- Or subscribe to your newsletter
Conversion is the ultimate result of your SEO efforts. You optimize your page to match user search intent because you want them to see your site, visit it, and take action on the CTA.
Tracking conversions can help measure your SEO progress by evaluating how effectively your strategies are driving desired actions.
While SEO may bring that traffic to you, your site must encourage them to convert to customers. This is the best way to know if your SEO strategies have been successful.
You can track your conversion with Google Analytics. With GA, Google refers to conversions as key events and explains how to create and edit key events to track your conversions.
Once you set it up, track your conversion rate with a few steps:
- Log in to Google Analytics
- Go to Reports — Acquisition, and navigate to Traffic Navigation.
It shows you a list of all traffic sources, the traffic coming in through each source, and the number of these traffic conversions into leads or customers (key events).
7. Technical SEO
For your website to rank, it has to be crawled by Google bots.
These crawlers follow links from one page to another on a website and gather data on the pages they visit.
Once a page is crawled, Google analyzes its content to determine whether it follows the E-E-A-T guideline, whether its structure is navigable by users, and its metadata to understand what it is about.
If your website passes this evaluation, it is indexed and stored in Google’s database. If it doesn’t, Google will not index your website, and a website that’s not indexed has little to no chance of ranking in SERPs.
This is why technical health is important.
Technical SEO modifies technical aspects of your website, such as its structure and site speed, to improve its visibility.
It makes it easy for search engines to crawl and index your website pages and shows Google that your website is accessible to users.
For search engines to index your website, you must have good technical health which includes:
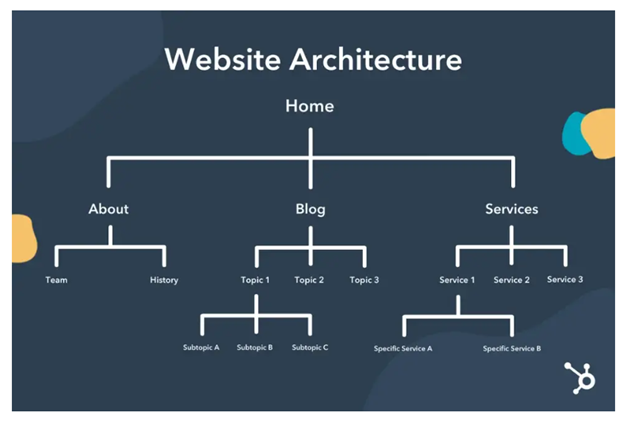
- Website structure
Google crawlers navigate your site with internal links. They go to a webpage on your site from a link on another page, which is why internal linking helps increase the visibility of your web pages.
It should look like this example from Hubspot:
- Mobile Optimization
Google now uses mobile-first indexing—if a user searches for a query on their laptop, Google will provide results based on the web version of the websites. This means if your website isn’t optimized for mobile devices, you won’t rank on Google.
Read more about mobile SEO to know why it is important for your website.
- Page speed
Page speed refers to how fast your page can load. The recommended speed is under 2 seconds—you risk a high bounce rate if your page loads slower than that.
To improve your technical SEO health, read this checklist for what to look out for.
8. Backlinks
Backlinks are quality links from other sites to yours, and they are important ranking factors.
It shows that other websites find your website helpful and reputable enough to link back to it.
Google even gives tips on how to build quality backlinks— it’s that important. This is why you must track your backlinks to know if you’re getting it right.
Tools to Measure and Track SEO Performance
- Google Analytics to check website traffic, analyze user behavior and track essential SEO metrics.
- Google Search Console to understand how Google sees your site (including keyword performance and technical issues).
- Rank tracking and third-party tools, like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz, to monitor your website keyword ranking progress.
- Other tools are PageSpeed Insights for site speed testing, and Hotjar for conversion rate optimization, etc.
Tips To Improve Your SEO Performance
There are three categories of SEO— on-page, off-page, and technical SEO. Your website needs to meet these three different standards to gain visibility in search results pages. Here’s how they help:
1. On-page SEO
On-page SEO aligns your website’s content with your audience’s search queries.
Effective keyword research is a crucial component of successful SEO strategies. It helps in understanding what prospects care about and identifies underutilized keywords, enabling a brand to enhance its online presence and drive organic search traffic.
It prioritizes optimizing web elements like your network descriptions, headers, title tags, and internal links. Some on-page SEO strategies include:
Content quality and E-E-A-T
Google uses E-E-A-T to assess the quality of your web pages and content.
- E stands for Experience. Google considers the author’s experience in the content they create. For instance, if you have a fitness blog, Google will favor content from someone who has real-life experience in fitness, like a personal trainer.
Share stories in your content, add testimonials, and talk about real customers. If you want to add recommendations or advice to content, make sure it comes from someone with experience using the product or service— like an existing customer.
- Expertise
Expertise refers to how knowledgeable the person creating the content is. Google will rank pages whose author has genuine knowledge—backed by education, training, or service—over the topic.
Tip: Hire or collaborate with industry experts to create content. For example, this post on WebMD about headache causes was medically reviewed by a certified medical doctor.
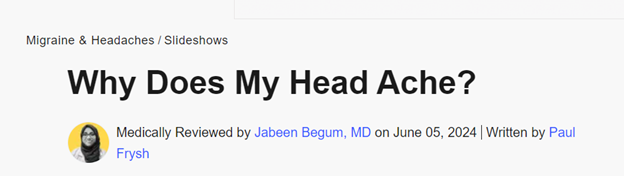
It shows users that every information on the page is authentic and can be trusted.
- Authoritativeness
Google focuses on your website’s reputation as a ranking factor. It checks if other websites are referring to or linking to your pages. Google rates your authority based on the number of your referring domains.
Tip: use a link-building agency to improve the quality of your backlinks or invest in guest posting to get mentions from other blogs.
- Trustworthiness
Google wants to know that users can trust your website, especially if you offer financial or medical advice. This means that you need to make sure your site is secure—use secure HTTPS encryption (that padlock in the browser), have a clear privacy policy, and provide accurate information. A good tip is to collect positive reviews from your customers and add them to your homepage.
Proper Keyword Use
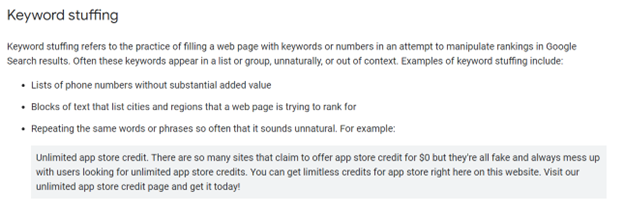
Keywords push your page to customers looking for related words and help you rank higher. Put your primary keywords in the title of your content, the headings, and the body text. But it’s important you don’t stuff keywords as Google considers it spamming.
Meta Tags and Headings
Meta tags are code snippets that give users information about your page. They help search engines understand the content of your page, which influences how your page appears in search results. Your meta tags include your
- Meta title: The title of your page that appears in search engine results. It should be concise and describe your page’s content. Adding your keyword is important here.
- Meta description: a summary page that appears beneath your title in search engines. It doesn’t directly impact rankings, but it can influence click-through rates— which is a win-win.
- Headings, on the other hand, organize your webpage structure so users and search engines can understand the main topics you covered. Break your content into Heading 1 and subheadings 2, 3, and 4 to make it easier to read.
2. Off-Page Optimization
Off-page SEO is an external effort focused on increasing a website’s authority and helping it rank higher on search engines. It primarily involves backlink building and content distribution (sharing your content on social media and forums).
3. Technical SEO Improvements
Technical SEO ensures that your website functions smoothly, loads quickly, and is optimized for user experience across all devices.
Conclusion
SEO increases your website’s visibility to web users. But before that, it needs to appeal to search engines —since they have the ability to rank your page. This is why it’s important that your website is accessible to both search engines (to find it) and web users (to engage it). Using the metrics mentioned in this article, you’ll be able to track your SEO performance and optimize where necessary.
