How to Tell if Your SEO is Working
SEO is the art of optimizing websites to rank higher in search engine results, making it easier for users to discover your content when they search for relevant keywords. Understanding whether your SEO strategies are effective is crucial, as it ensures your site appears prominently whenever someone searches for topics you’ve covered.
So, how do you know if your SEO is working? Which metric should you be looking at to measure your SEO performance?
SEO is a long-term strategy, often requiring at least three months to start showing noticeable results. In some cases, it may take up to a year to observe more significant outcomes. To gauge the effectiveness of your SEO efforts, let’s explore the key indicators you should look for after running your campaigns for approximately three months.
Key Metrics to Measure SEO Performance
Measuring your SEO performance is about knowing the efficiency of your strategies and how well your website ranks in Google. Some of the valuable metrics to know you’re heading in the right direction include:
1. Your Organic Traffic
Organic traffic is the number of visits your site gets from search engines. It’s organic because these visits are not from ads and other forms of pay-per-click advertisements.
If a potential customer searches for “blue bags for fall outfits” and your fashion page on bags for different seasons pops up on the SERP, they’ll be visiting from search engines organically.
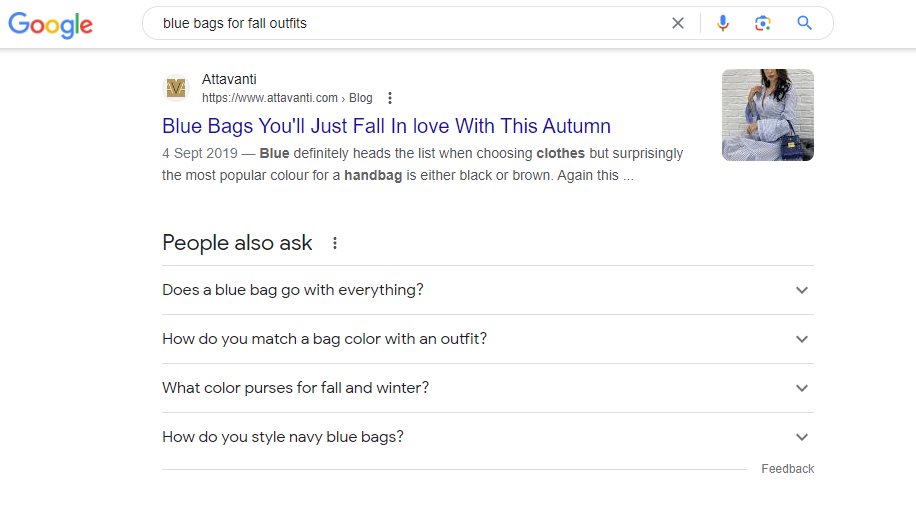
Your organic traffic shows how well your web pages rank on search engines for relevant keywords. It also shows how much quality traffic you can get from those keywords.
To check this metric, log into Google Search Console and head to Performance to see your organic ranking for the duration of your choosing.
You can also use paid tools like SEMRush, Moz, or Ahrefs to track this.
Tracking organic traffic lets you know if your SEO efforts are right on track or if they need a complete overhaul.
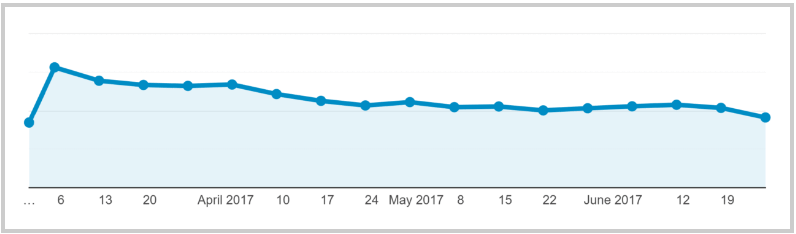
Your strategy would usually need a complete overhaul if your organic traffic looks something like this:
2. Your Conversion Rate
Your conversion rate is the number of users who completed an action you wanted them to take.
This could be the number of web users who subscribed to your newsletter, signed up for a free trial, downloaded your eBook, or bought a product.
The conversion you’re looking for could also be considered leads.
If your SEO strategies aren’t bringing in leads, you’re doing it the wrong way. Tracking conversion rates helps you know if your content converts as expected.
A quick way to track your conversion rate is by calculating the number of conversions (downloads of an eBook, subscribers, the number of people that bought a product) divided by the number of visitors.
If your page received 200 visitors in a month and has 70 sales, your conversion rate is 70 sales divided by 200 visitors or 35%.
Another easy way to track and set it up is by following the process highlighted by Google in this video:
3. Your Search Engine and Keyword Ranking Matters
Your search engine ranking shows how often your website appears on SERPs for relevant keywords.
Keyword ranking, on the other hand, is your website’s position on SERPs for a particular keyword.
The gist is that the higher you rank on keywords, the higher your site’s traffic. This doesn’t mean you’ll automatically get clicks; it means your website is visible on the search engine (which is where search engine ranking is essential). It also means your web impressions will increase.
Tracking your search engine and keyword ranking informs you of your valuable keywords. The higher these keywords rank, the easier to get organic traffic and achieve your bottom line SEO goals: sales.
If the keywords you optimized to rank aren’t ranking, this metric can also help you evaluate your competitors’ strategies to see how you can improve your performance on search engines.
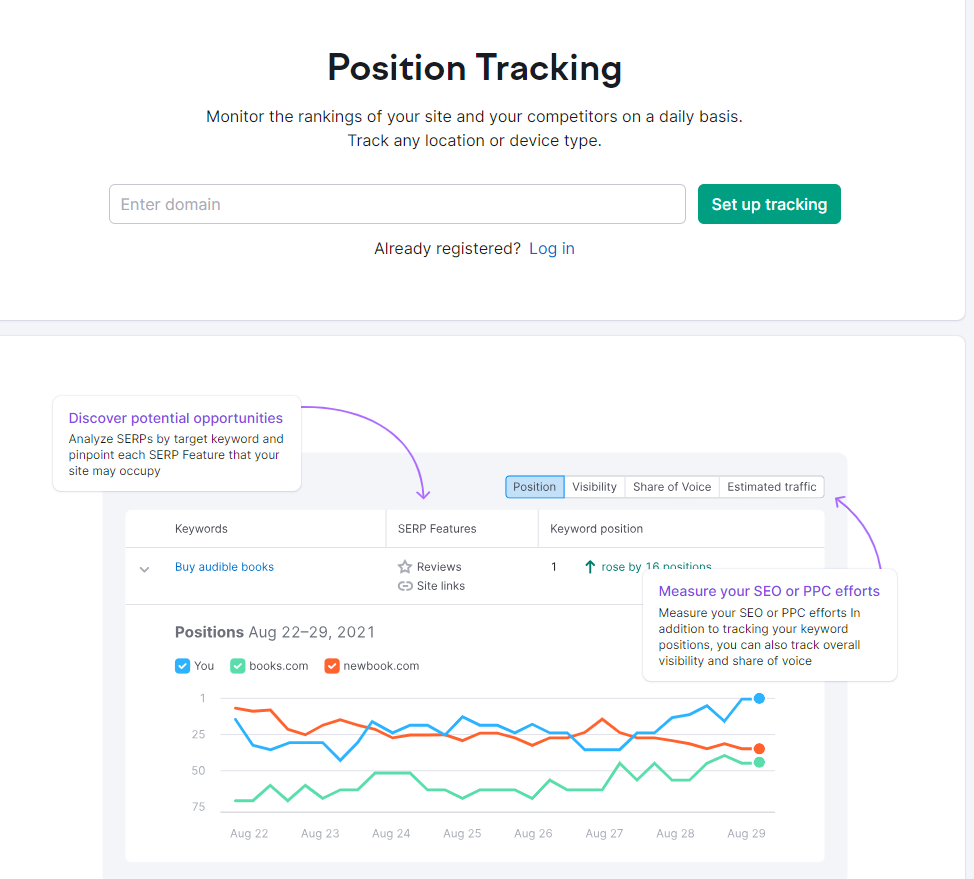
To check your keyword and search engine ranking, use tools like SEMRush’s Position Tracking tool, Rank Tracker, Ahrefs, MozPro, or SEOquake. SEMRush’s tool looks like this:
4. Build Domain & Page Authority
Domain authority is a reputation score for websites. It shows how likely a website will appear high in search engine results.
A website with high domain authority is like a well-respected expert in a town— people are more likely to come to you for industry advice because many other reputable sources have recommended (or linked to) you.
Your domain authority and page authority are determined by the quality of the content on your blog, the quality of the backlinks you’ve received so far, and how long since you started publishing content.
While domain authority means the quality of your website, page authority refers to the quality of a single webpage on your website.
Tracking these two predicts your performance on search engines because the higher the domain authority, the easier it is for your website to rank on SERPs.
Use tools like Moz’s Free Domain Authority Checker, SEMRush’s Domain Overview, and Small SEO Tools Domain Authority Checker to check your domain authority.
These tools will rank your website on a logarithmic scale of 1 to 100. There is no “best domain authority calculation.” A score between 40-50 is average, and a 50+ score is much better.
If your score is low, what do you do?
- Create high-quality content and intensify distribution so industry fellows can know about you, read your content, and link out to it;
- Guest-post on industry blogs and link out to relevant pages on your website;
- Create industry reports so that blogs and experts can link out to your page when they’re quoting the data in your report.
5. Consider Pagespeed & Mobile Optimization
Page speed indicates how fast your web pages load, regardless of the browsers or devices a user uses.
According to Google, your website’s bounce rate increases by 32% when the loading time exceeds two seconds. The average human attention span is getting shorter, and your page should load faster.
You can improve your page speed by:
- Using a content delivery network (CDN) as part of the features of your cloud services;
- Compressing your images.
Read about other technical SEO fixes you can make on your website here.
Aside from pagespeed, optimize your website for mobile. Over 92.3% of internet users access the internet via mobile, and over 55% of web traffic comes via mobile.
Your bounce rate will increase, and you could lose valuable customers if your web isn’t navigable via mobile.
To ensure your website is optimized for mobile, go to Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test—type in your website’s URL, and test for mobile optimization.
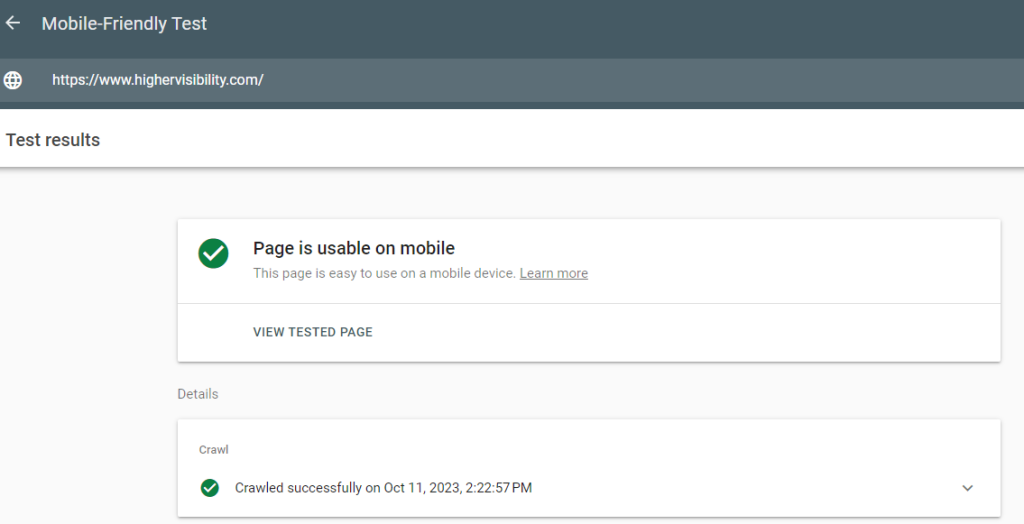
6. Check Relevant Keywords & Competitive Keywords
Relevant and competitive keywords are two vital players in the SEO game. Relevant keywords are those terms and phrases that relate to the content, products, or services your target audience is searching for.
Your page ranking for “eco-friendly bamboo toothbrushes” gives more specific details on the kind of product you have. It’s relevant to search intent, and a longer tail keyword can even convert faster.
Competitive keywords, on the other hand, are the more extensive ones.
They are keywords that your competitors also (want to) rank for because they have high intent, high keyword difficulty, high traffic, and high conversion potential.
An example that matches the eco-friendly bamboo toothbrush could be “x sustainable home products.” This is more competitive because your competitors want to showcase their products, optimize for SERPs, and rank.
You can use these two metrics to gauge your SEO performance. To achieve that, you’d need to:
- Know the vital keywords your business needs.
- Check how well these keywords rank in SERPs compared to your competitors. You can use SEO tools like Google Analytics to track changes in ranking.
- Incorporate these keywords in your content writing efforts and monitor your traffic.
- You can also use relevant long-tail keywords to gain more quality traffic and leads to your website.
To track relevant keywords and competitor keywords, use a paid SEO keyword-checking tool to filter keywords by industry (or from your competitors) to see what they’re writing about.
7. Bounce Rate & Average Time on Site
Your site’s bounce rate is the number of users who visit your site and leave without interacting or navigating to any other page.
This could mean that they only read one blog post, they didn’t click on a link to another page, fill out a form, or perform any other action. They came and left.
The bounce rate metric helps you know if visitors find your web pages helpful or not.
Some of the factors that lead to a high bounce rate include
- Slow page speed
- Lack of quality content
- Hard to navigate website
- Ineffective call to action
Monitoring your bounce rate and the average time a user spends on your website reveals the weaknesses of your SEO campaigns and your technical SEO.
However, a high bounce rate isn’t always a red flag. If you’re creating content for visitors to absorb and exit, a high bounce rate is expected.
But if you want them to take action, then watch out for the metrics to readjust where necessary. You can use Google Analytics to check your bounce rate by following this simple process:
- Set up your Google Analytics page if you haven’t. It’s a popular and free choice.
- Log into your website’s Google Analytics dashboard, go to the ‘Audience’ section, and then to the ‘Overview’ subsection. This will provide an overview of your website’s visitor data, including the bounce rate.
- Check the bounce rate. The bounce rate will be displayed as a percentage. This percentage reflects the portion of visitors who landed on one of your website pages and exited without interacting with other pages.
- Analyze bounce rate by pages or segments. You should see the bounce rate for specific pages or different segments of your audience. You can do this by navigating to the ‘Behavior’ section and then to the ‘Site Content’ subsection, where you can view the bounce rate for individual pages.
- Interpret the data: A high bounce rate could indicate that the page isn’t resonating with your audience, while a lower bounce rate suggests visitors are more engaged and are exploring more of your website.
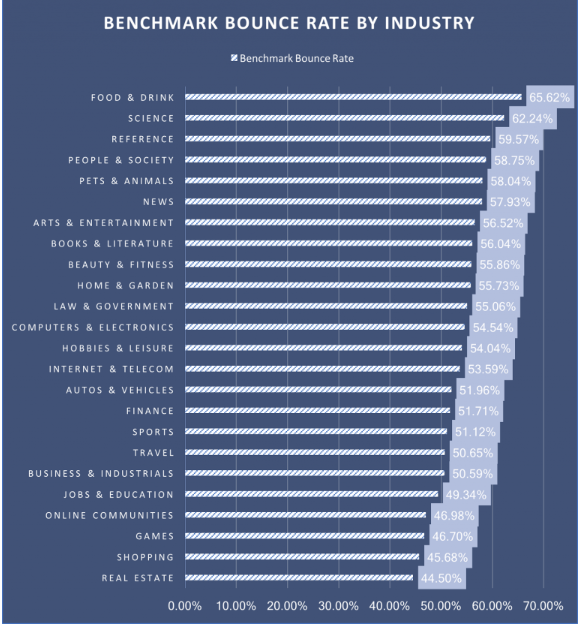
Note: bounce rates are influenced by the type of website, the industry, the source of your traffic, and the expectations of your visitors when they click on your content.
Here’s the average bounce rate based on your industry:
8. Are Your Backlinks and Referral Traffic Increasing?
You already know what backlinks are: They are the links to your pages from other websites. Having quality backlinks from reputable websites leads to good referral traffic.
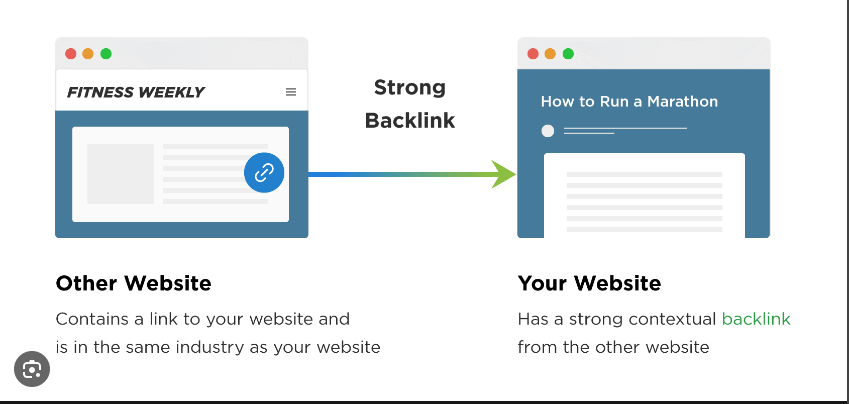
You may find that your backlinks are high, but you’re not getting any traffic. That’s courtesy of quality.
Buying cheap and low-quality backlinks from Fiverr or using pay-for-performance SEO methods won’t boost your SEO performance.
Instead, focus on creating quality content that’ll make people want to refer to your pages, and you’re good to go.
Best Practices for Measuring SEO Performance
Implementing an SEO strategy is not piecemeal. Great SEO campaigns take time to show results. In the meantime, these are some of the best practices to monitor your growth and check for weaknesses:
Use Google Analytics and Other Tracking Tools
Google Analytics is a go-to tool for monitoring your performance metrics.
It can be integrated with Google Search Console to uncover several trends and patterns in how web users interact with your web pages.
You can also use free and paid SEO tools like SEMRush, Moz, Ahrefs, SE Ranking, and Google Pagespeed Tools.
Monitor Organic Keyword Rankings Regularly
Monitoring your keyword rankings must be a consistent activity to track the success of your SEO efforts so you can adjust where necessary.
For example, monitoring your organic traffic lets you know which pages have declined or are no longer getting the clicks they should be getting. This usually happens after changes in Google’s algorithm or your competitors create content that fills more gaps and ranked more.
Tracking keyword rankings lets you know whether to update your content, add relevant images, schema markups, or optimize for mobile.
To set up a recurring monitoring system, choose an SEO tool. This could be Google’s Search Console, Moz, or SEMRush, among others.
Then, you set up tracking. How?
Enter the keywords you want to track into the SEO tool you’ve chosen. Some tools, like Moz Pro and SEMRush, will let you add keywords to your project manually to track their rankings. Other tools, such as Google Search Consoles, automatically add your keywords.
Once the keywords are in, schedule regular reports — daily, weekly, or monthly. You can then analyze the reports the SEO tool generates and adjust your strategy based on the results.
PS: Rankings can fluctuate frequently, so look at long-term trends rather than little daily changes.
Actionable Insights from SEO Data
Every metric, from organic traffic to the quantity and quality of backlinks your site gets, depends on data. Now, data is accessible, how do you convert it to improve your SEO performance?
Translate Data into SEO Strategy
Identify the gaps and opportunities that could be in lower metrics.
If your domain authority is decreasing, guest-write with reputable websites and link to your pages. If you’re not getting enough traffic, look for content gaps, maximize meta tags, and improve your technical SEO.
Don’t stop there. High bounce rates can show that your content isn’t meeting your audience’s expectations. Put yourself in their shoes and compare your page to your competitors’ pages to find out what’s wrong.
You can also examine data about the quality of your backlinks to identify patterns in the type of sites linking to you.
This lets you evaluate quality links and intensify your outreach and guest-posting efforts.
The goal of backlinking is to ensure that authority sites link to your web pages to increase their value and eventual performance on SERPs.
Continuous Improvement Cycle for SEO
Data can help improve your SEO efforts.
It shows the things your site is doing wrong (which is why you’re not getting enough results from your efforts).
This is why you should set clear goals based on your data. Take action based on these goals. These actions could be anything from updating your content to suit the changes your data reveals or enhancing mobile friendliness to help users navigate your website easily or stay on your page more.
Implement your changes and monitor your metrics to see the impact.
For instance, track keyword ranking and conversion rates months after creating more content with high commercial intent keywords (with effective calls to action) in your content library.
Ultimately, comparing your stats to your competitors’ is an effective way to measure your growth. Check for the kind of content they’re publishing, the categories they’re addressing, and if you could create related content.
Rounding Up
SEO is a long but rewarding journey. The more you pay attention to the metrics that matter, the better for your business because it’s the only way to track the performance metrics that convert to bottom-line revenue.
Remember, Black hat SEO techniques may give you fast results, but these results are often short-lived. Ethical SEO practices ensure that your efforts are built on a solid foundation, provide value to your audience, and maintain the integrity of your website.
Google rewards ethical SEO practices with the performance you expect; you only need to track them to know what’s working and what isn’t. what needs adjustment in your SEO strategy.
Understanding the impact of your SEO efforts is crucial. Let our experts analyze your performance and provide actionable insights. Request a tailored proposal today and ensure your strategy is on the right track.

