How Often Should You Update SEO?
Editor’s Note: This post was originally published in December 2023 and was updated in September 2024 for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Your SEO strategy needs to be revamped every three to six months because if you keep doing the same thing, you’ll see the same results. That doesn’t mean you shouldn’t experiment or give your campaigns time to show real results — it means you need to know when to shift gears to pursue newer marketing objectives.
For instance, targeting high-intent keywords is a smart strategy for attracting and converting people looking for your product/services. However, high-intent keywords often have low traffic.
If you have achieved sufficient success through signups and other KPIs and want to increase organic traffic (for brand awareness), create pillar pages with high-volume keywords and link to them. These drive more traffic than the typical high-intent, bottom-of-the-funnel, low-volume keywords.
With this strategy, you can still link to your high-intent and high-value pages to refer visitors and demonstrate your product’s value.
In this article, I’ll explain why SEO is an ongoing process and the signals to look out for to optimize your SEO strategy.
Why is SEO Strategy an Ongoing Process?
For many reasons, but here are some leading reasons why SEO strategy isn’t static;
- SEO algorithms are constantly changing: Google and other search engines update their content ranking standards through new updates every time. Google, for example, is keen on improving user search experience, which means they invest a lot in algorithms that spot helpful content and reader-friendly web pages.
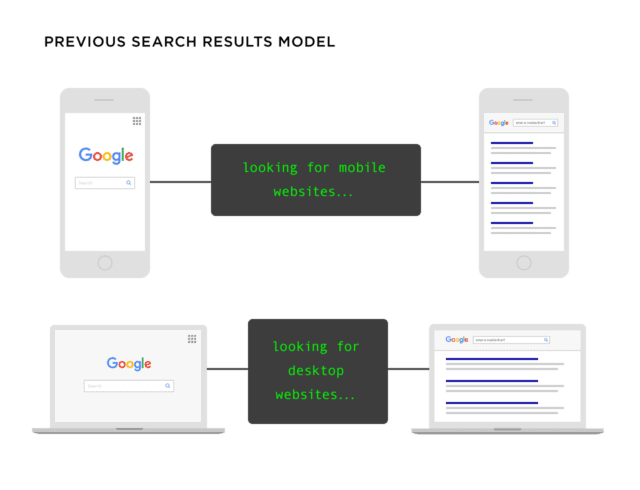
Before 2023, Google ranked websites based on whether they were optimized for desktop or mobile. If your website is optimized for desktop, it might rank for desktop users but won’t for mobile users. The previous model had this structure:
- Optimized on mobile = rank on mobile devices
- Optimized on desktop = rank for desktop users.
Here’s a Backlinko illustration:
However, since October 2023, Google has fully transitioned to mobile-first indexing. This means that if your website isn’t optimized for mobile devices (but is optimized for desktops), it will not rank for desktop and mobile searches. It looks like this now:
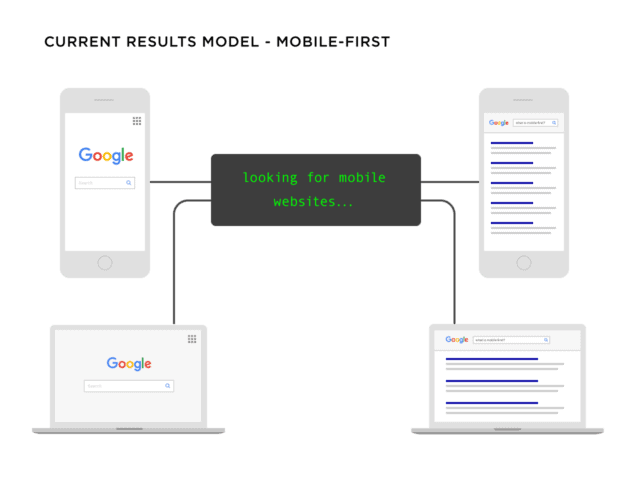
Google chose mobile-first indexing because “mobile web traffic has continued to grow…people almost exclusively use their phone to access the internet.”
At the time of writing this piece, Google has rolled out two core updates (amongst other minor ones) in 2024. And there should be more before the year runs out.
If you are unaware of these updates and how they can affect your visibility on search engines, your website may slowly slip to the second or subsequent pages on SERPs, like some 44% of SEO managers in a survey. This won’t be good for your business.
- Consumer search preferences are never the same: The growth in voice and image searches presents new opportunities to rank for new keywords and attract more quality traffic. For instance, you can add alt texts to your images to rank more for image searches. But if you don’t know this, you may not be able to optimize all your media assets to rank on Google.
Another thing to consider is that the user journey isn’t linear. It’s rare to see a customer convert on the first visit unless you’re a well-established brand and attract branded searches. You need to understand user search behavior, what they’re looking for (in terms of content), and what influences their purchase decisions.
For example, a B2C buyer would be more interested in seeing reviews from other customers before purchasing. So, let your SEO strategy include user-generated content on high-converting pages.
B2B buyers, on the other hand, are more likely to search for case studies or white papers that demonstrate the value and ROI of the product/service before paying for it. Learn these nuances and factor them into your strategy.
- Optimizing for generative AI tools: Tools like Perplexity AI get insane traffic every day. Google’s use of AI overviews is also a threat— users find the results they want faster without going through any web pages. In some cases, Google’s AI overviews and Perplexity AI recommend websites users should read more from.
Ranking online also extends to being cited as a relevant source on generative AI search engine tools. This means that aside from your SEO strategy to target relevant keywords or optimize the website, you also need to cater to these AI tools.
Why?
Perplexity AI gets over 82 million visits a month and provides at least 5.28 citations that can drive a ton of traffic to your website. So, having a strategy to feature in these tools’ search results is also why SEO strategies change.
- The competitor effect: You’re not the only one vying for the top spot on the SERPs. Your competitors are working to achieve the same. This calls for consistent competitive analysis when creating an SEO strategy for your business.
How Often Should You Update Your SEO Strategy?
You should update your SEO strategy as often as you can.
However, don’t take our word for it. Every brand has different goals that decide how often they update their strategy.
If your goal is to convert traffic and increase revenue, you’ll create content that targets the “ready-to-buy” customers. You’ll also want to optimize your product pages and improve conversion funnels to improve click-through rates.
If you want to generate traffic and find ways to convert them, target high-volume keywords and filter them with high-intent keywords. This helps you increase organic traffic while targeting people interested in your product/service. If this is the goal, update your strategy at least once every six months to find new keyword opportunities and approaches to content.
Signs You Need to Update Your SEO Strategy
Observing your SEO performance is an easy way to know what’s happening in the backend. Here are some of the things you’d identify before you analyze and update your strategy:
1. Your content is in the ‘plateau’ or ‘decay’ phase:
This analogy from Ryan Law, VP of content at Ahrefs, and Jimmy Daly, CEO of Superpath, gave an interesting analogy on content growth. According to them, every blog post passes through five stages:
- The spike phase
- The trough phase
- The growth phase
- The plateau phase and
- The decay phase
Here’s a graphical illustration to help you understand better:
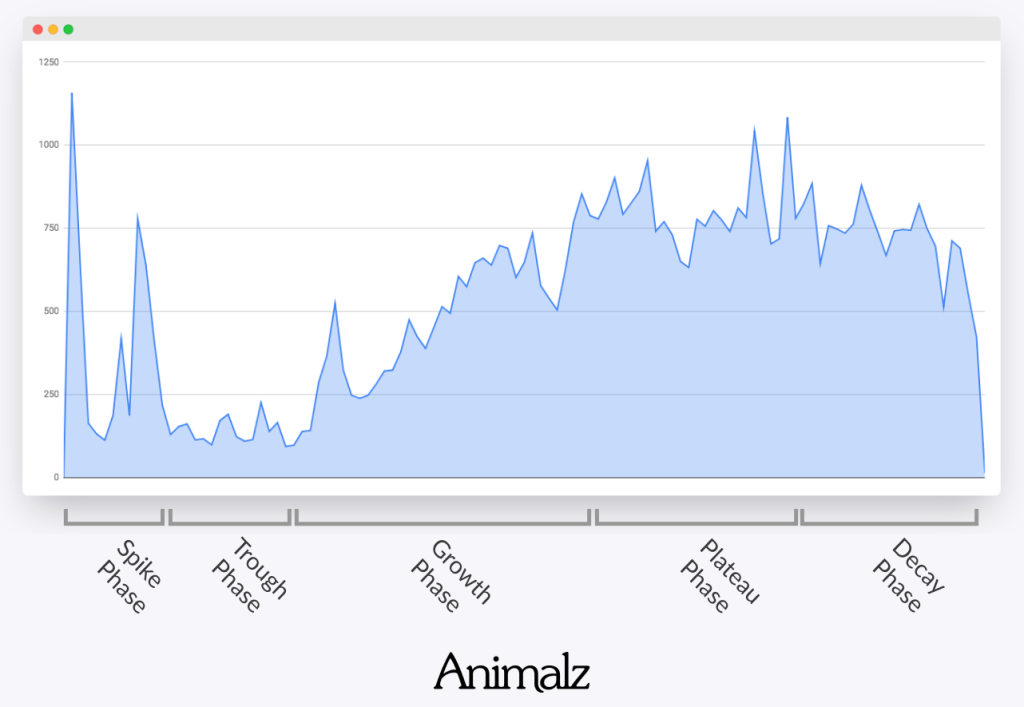
As you can see, the plateau and decay phase is the moment when your content starts to lose relevance in the search results, i.e., it doesn’t cater to user search intent (as it used to), or your competitor’s article is better (they probably covered new angles in their blog posts).
Refreshing your content – or, better, your overall SEO strategy – can help you grow more traffic. In fact, “freshness” is one of Google’s indirect ranking factors, as they prefer that your pages be updated regularly, especially if your target keyword demands it.
A good start is to take inventory of all your web pages. Conduct a site audit to find technical and on-page issues like broken (or outdated) links, keyword gaps, slow site speed, etc. Also, if you’ve recently published a blog post, run a quick check after three weeks or one month to gauge its performance. If you notice:
- Traffic has been declining steadily month over month
- Contributes only a minute portion of your website traffic
- There are a lot of areas (in terms of keywords) left uncovered
… then it’s a sign your web content needs an overhaul.
Note: A content “refresh” is most important when targeting search queries that require it regularly. For example, if you’re selling electronic gadgets, you’ll need to publish content (or update) whenever a new model is released. This is subjective, and it only gives you an idea of how often you should update your SEO.
What to do:
The goal isn’t to update your content to ” outperform the competition” or “drive better traffic.” Instead, it should focus on your target audience and give them the best (and most enjoyable) experience on your site. This may demand refreshing your web pages once or twice every month. As I shared earlier, it depends on your data and target keyword.
You can also use heat maps or session recording tools to see how users interact with your content and which section they spend the most time on. This gives you an idea of which areas are most engaging or need improvement (where they drop off, for example).
2. A decline in organic traffic
This point goes without saying. When you notice anything unusual about your organic traffic (except if you’re targeting seasonal keywords), check out your website to learn why.
A traffic drop can be a result of any of the following (or a combination of two/three):
- An algorithm update
- Server downtime
- Seasonal trends
- Your competitors are winning for your keywords
- Website revamp (it’s normal to experience fluctuations after a revamp)
What to do:
The first step is to verify the reason for your traffic loss. Google Analytics (better if you use a third-party SEO tool like Ahrefs) provides a glimpse into your traffic over time. You can adjust the dates to the last quarter or year to get a comprehensive view of your website traffic.
Take a look at the pattern, too. Did the traffic decline steadily, or was there a sharp drop? An algorithm update could cause a sharp decline; it could also be that most of your traffic was from seasonal keywords that are no longer sought. It shows like this:
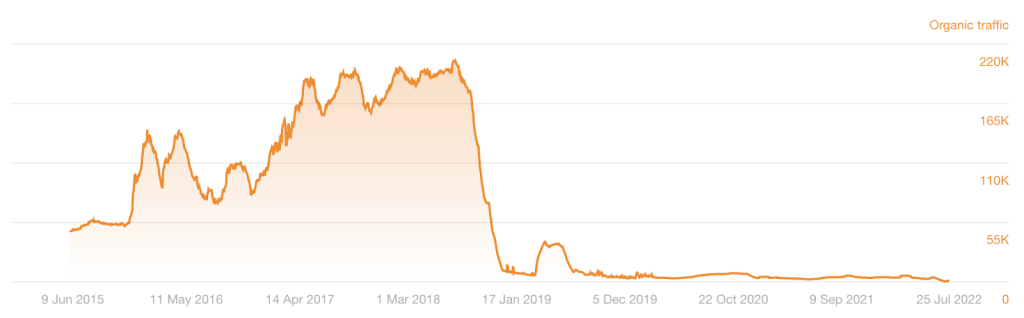
If the traffic decline is steady, it could be due to technical SEO issues, lost backlinks, or subpar content that doesn’t cater to user search intent.
Once you can identify these issues, use a working strategy to address the issues and re-optimize your site. Read more about how to analyze and troubleshoot a traffic drop here.
3. When you lose your ranking spot to your competitors
You’re topping the search results for your target keyword, and boom! Three competing websites suddenly outrank you. No, it’s not a mistake. It only shows that users find these competing pages more “relevant” than yours.
Remember, Google cannot understand web content but can determine “relevance” by checking user engagement metrics. For example, high dwell time and session duration indicate that users find the page helpful. See this point on Google’s website about “content relevance.”

So, once you notice your website (or high-value pages) are slowly slipping to the bottom of the search results, it’s time to tighten your seatbelts. You need an SEO update.
What to do:
The first thing to do is review your competitor pages. They might have more updated and comprehensive content or target new keywords that capture what searchers are looking for. Conduct competitor analysis to discover what they’re doing and what you’re not.
Also, read their content. What keywords are they ranking for that you can also optimize for? Can you take another approach to improve content quality and its value? While evaluating their strategy, look out for gaps that can help you improve outcomes.
4. Your keyword performance:
Are you currently ranking for your target keyword? If yes, what position are you in on the search results? You need to update your on-page SEO if you’re not anywhere in the top three results or on the first page.
According to recent statistics, the top three Google search results get 54.4% of all clicks.
This means 45.6% of clicks are split among the subsequent pages. And if your site is on the second page, you might not get enough traffic, especially if SEO is your primary client acquisition channel.
The way out?
Always ensure your keywords are relevant to user search intent. The recent Google helpful content update prioritizes helpful, original, and people-centered content. And using the right keywords in your content can help you rank for the relevant search queries.
What to do: When researching keywords, look for those that will give you the maximum impact. Ensure you understand the search intent behind the keywords and write quality content that will engage readers. You can also
- Use Reddit, Quora, and Google Trends to see what topics matter the most to your users.
- Focus on long-tail keywords since they have more precise search intent than short-tail, generic keywords.
For example, instead of searching for ‘iPhone,’ consider ‘pre-owned iPhone 14 pro max for sale.’ While the latter will have a lower search volume than the former, it’s more detailed, and targeting keywords in this category helps you create a content strategy that brings you closer to (potential) customers. Plus, thanks to their lower search volume, these keywords have a low difficulty score and are easier to rank for.
Pro tip: If you have many pages on your site, ensure you check for multiple pages ranking for the same keyword. This is called keyword cannibalization and can affect your search engine rankings because Google won’t know which blog post to index. Tools like Google Search Console or Screaming Frog can help you find these pages and re-optimize them.
5. Poor conversion rates
Traffic is good. But we both know conversion is better. After all, what’s the benefit of topping the search results if your efforts aren’t impacting bottom-line results?
A drop in conversion rates (or zero conversions from content) is a clear sign that you’re either publishing the “wrong” content or your CTAs aren’t converting readers.
Your website’s user experience also matters. Adding functionalities like new CTAs (calls to action), bigger buttons, high-quality images, etc., can impact how users (and search engines) use and navigate your site. This means you can see an increase or decrease in conversion/traffic.
What to do:
Whenever you make these changes, monitor whether they improve web performance and conversions compared to the previous design. You can effectively do this through A/B or usability testing tools. Learn how to generate more leads here to improve your conversion rates.
6. Search engine algorithm updates
Search engines like Google and Bing are constantly releasing and refining their algorithms. Google, for example, releases at least 600 updates per year! These changes can impact your web content and cause your site to lose traffic. If you notice fluctuations in your web traffic after a significant update, it’s a clear sign that you need to evaluate your strategy.
What to do:
Don’t beat yourself up if a major update has hit you. Instead, check out the requirements on Google’s website (or the search engine you’re using) and update your SEO strategy accordingly.
7. Evolving user intent
As technology advances, customer behavior online is similarly changing. The intent behind specific keywords and search queries also evolves as this happens.
For example, a user searching for “best wedding dress” years ago might only be looking for ideas. Now, Google looks at the user intent by checking previous browsing history and location before serving pages in the search results. Because the user might not be looking to buy a wedding dress now, they might want to be looking for styles and trends.
Tip: Revisit your SEO strategy at least quarterly and conduct regular SEO audits to discover issues that can be resolved. SEO audits are essential if you have many content pages that need to stay relevant in search results.
Keep in mind that the frequency of your audits depends on:
- The size of your website: the more your web pages, the more regular your audits should be to discover any impediments against performance.
- Changes in user behavior on your site: If you add or remove some functionalities on your site, monitor how they affect (or improve) user engagement. Use A/B testing to monitor these changes before implementing them permanently on your website.
There are many other things to consider, but these two are important when preparing for your audit.
A better option to help with the process would be to partner with an agency. We at HigherVisibility spend quality time analyzing issues with your technical SEO. This helps us uncover issues affecting your visibility and create an action plan that addresses them. We offered technical audits as part of our services for Fitness19, and it led to a 383% increase in organic traffic and an 1844% increase in conversions. Read the full case study here. Learn about our services here and partner with us for better results.
8. Missing or Duplicate Title Tags
Title tags have a direct influence on your click-through rate. It’s the first thing searchers see when they run a query, so you need to ensure they’re compelling and “click-worthy.”
Although Google’s John Mueller shared that page titles are irrelevant for rankings compared to the page’s primary content, it’s still worth optimizing to encourage strong organic click-through rates.
What to do: Conduct an on-page SEO audit using tools like Screaming Frog to evaluate your site and identify pages without title tags or duplicate titles (especially if you’re constantly adding new or updating your web content). Then, replace them with compelling, accurate, and optimized ones.
Some tips for creating an SEO-friendly title tags are:
- Place your primary keyword at the beginning of your title
- It shouldn’t exceed 60 characters, and 600-pixel limits
- Communicate ‘what’s in it for me’ by adding the benefits users stand to gain
- Use freebies to incite a click-through. E.g., ‘How to create a user persona for SEO (with a free downloadable template)
- Ensure it is relevant to your page content
Tip: If you have content with dated tags, always update the title tags to the current date. For example, the title, ‘How often do you find keywords for SEO in 2022,’ looks stale in 2024.
9. Slow page loading speed
Website speed has been listed as one of Google’s core ranking factors since 2018.

They also confirmed here that their ranking systems “look at page experience aspects like a mobile friendly content that loads quickly.”

This means websites with slow page speeds are often de-ranked in search results.
What to do: Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights or Search Console to identify pages with slow loading speeds. SEMrush or Ahrefs gives more robust insights into your page performance – the issues affecting your page speed and how to resolve them without help from an expert.
Read more: How to optimize your website performance for increased visibility.
Conclusion: How Often Should You Monitor SEO?
I recommend conducting SEO audits quarterly.
For websites with more pages, you may want to update them more frequently, but you don’t need to monitor your SEO every day.
However, here are ten metrics you should track weekly to see how your SEO efforts are paying off:
- Keyword rankings
- Organic traffic
- Conversion rate
- Engagement rate
- Time spent on page
- Bounce rate
- Click through rate
- Domain Rating / Domain Authority
- Referring Domains
- Core Web Vitals
All of these metrics are accessible on your Google Analytics and Console account.r 15 years we have helped hundreds of businesses succeed in SEO. Let us do it for you! Request a free custom strategy today.
