E-Commerce SEO Best Practices for 2025 (Guaranteed to Boost Sales)
Editor’s Note: This post was originally published in March of 2023 and has been updated in March 2025 for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Every online store wants more sales. And organic search traffic is one of the most reliable ways to get them.
But here’s the challenge: 44% of online shoppers start their product search on Google, and 41% will rather start their search through a specific store (say, Amazon). If your store doesn’t appear in those search results, you’re missing out on potential customers ready to buy.
That’s why e-commerce SEO matters in 2025. And it’s not just about ranking—it’s about capturing high-intent buyers who already have their credit cards out.
This guide will show you how to:
- Build a site structure Google can easily crawl and index, for potential customers.
- Optimize your product and category pages to rank higher.
- Fix technical issues that hurt your visibility.
First, key elements of e-commerce SEO.
Key Elements of E-commerce SEO
Your website must have all of the following in its set-up to benefit from the potential of organic search:
- Keyword research: Understand how your target customers search for you and your products online, including the words they search for, and how they search for them.
- On-page optimization: Optimize your web pages with these keywords to increase your visibility on the SERPs.
- Off-page optimization: Improve your website through activities “outside” your website. For example, you can use link building and PR to increase your website authority and your ranking potential.
- Technical SEO: Optimize your website’s overall performance to improve user experience and increase your rankings.
- Google Shopping: Optimize for the free listings in Google Shopping. Read more for details on how to optimize your e-commerce SEO for Google Shopping.
I’ll explore these different elements in this article.
9 E-commerce SEO Best Practices to Improve Your Visibility in 2025
Since HigherVisibility started as an agency in 2009, we’ve worked with e-commerce brands like Fellow Products, Fastenere, and Diamond K Brass, and the following tips have always worked for us:
1. Start with Keyword Research
This isn’t to exclude the importance of a full website audit to know your technical SEO health and understand whether your website is well-designed for conversion.
But after that is done, your keyword strategy determines your store’s success in today’s search engine. Here are the results our client, Diamond K Brass, got from SEO within a one-year period.
You can see that paid ads (orange) brought fewer users compared to SEO (blue).
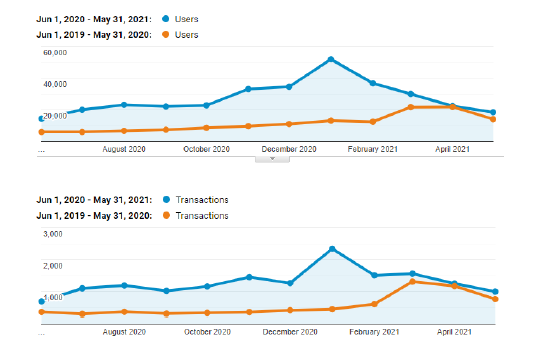
Of course, this declined a bit because the client tried another agency, but we had peak traffic and conversions through SEO over paid ads:

However, e-commerce SEO keyword research works differently than other types of SEO. You need to focus on transactional and commercial keywords that show buying intent.
How do you recognize these keywords?
Every keyword falls into one of these four intents:
- Transactional keywords. Used by searchers ready to buy or take the desired action. Examples are “where to buy clear ugg boots,” “ where to register for Glo yoga classes,” or, more specifically, “buy gaming laptop online”.
- Commercial keywords. Used by searchers who are ready to buy but want to educate themselves to make an informed decision. You’ll see words like “reviews,” “best [keyword],” “(product 1) vs (product 2),” and “best gaming laptops 2025”.
- Informational keywords. Used by searchers who want to learn about a product or service. Keywords have “how to,” “why,” and “what is,” variants. For example, “how to choose a gaming laptop”.
- Navigational keywords. They’re from searchers looking for specific brands. Examples are “Lenovo laptops” or “Fellow Stagg electric kettle”.
For e-commerce SEO, prioritize transactional and commercial keywords. These searchers are closer to making a purchase.
The best practice to find these types of keywords is through Amazon, Google search autosuggestions, and third-party SEO research tools.
To use Amazon and Google autosuggestions, start by typing your main product category into Amazon.com’s search bar. For example, for Fellow Products (our client), this could be “pour over kettle” or “coffee grinder”.
Amazon will suggest terms that past shoppers use in the autosuggest:
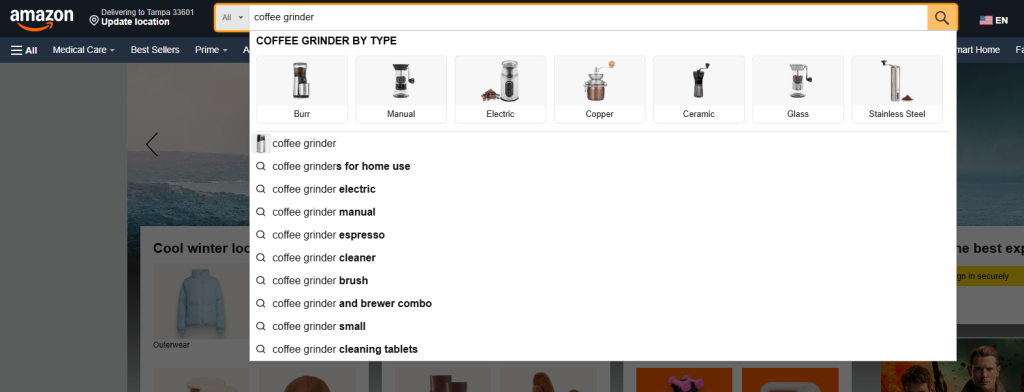
You can add “for” to find more options on what people are typically looking for on Amazon:
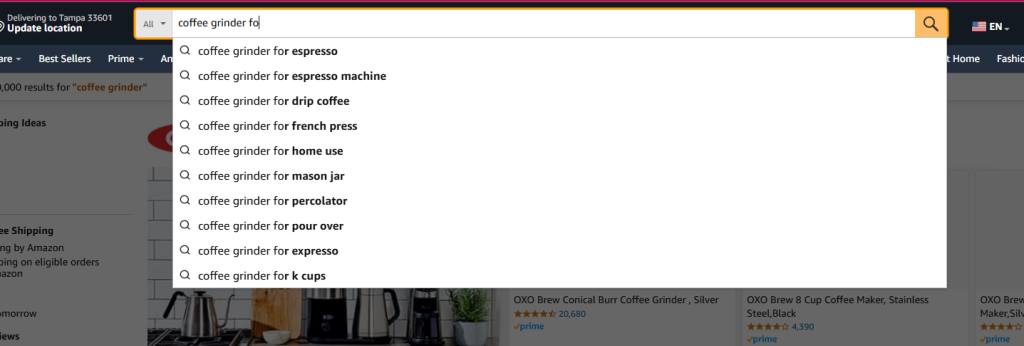
Do the same on Google, but add modifiers:
- Add spaces after your term: “coffee grinder ” shows different suggestions:
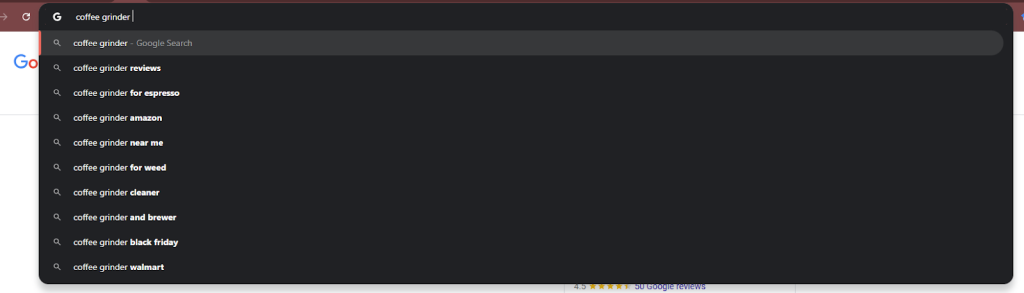
- Add letters: “coffee grinder a” reveals new keyword ideas:
- Add question words: “which coffee grinder”
You can also pay special attention to the “Related searches” section at the bottom of Google’s results.
The goal is to find valuable transactional and commercial keywords, if any, that you may have missed. Keywords that can convert ready-to-buy searchers if you rank for them.
Aside from using Amazon and Google Autosuggest, you can also use Shopify, eBay, and keyword research tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush and keywordtool.io to find keywords you can optimize your website for. Afterwards, optimize your page for the right keywords.
But before I discuss that, you need to learn how to conduct competitor analysis and steal from their strategy.
2. Analyze Competitor’s Keywords
Let’s say you’re Fellow Products competing against other premium coffee gear brands like Bodum and Hario. Here’s how to find their winning keywords:
Identify the top competitors:
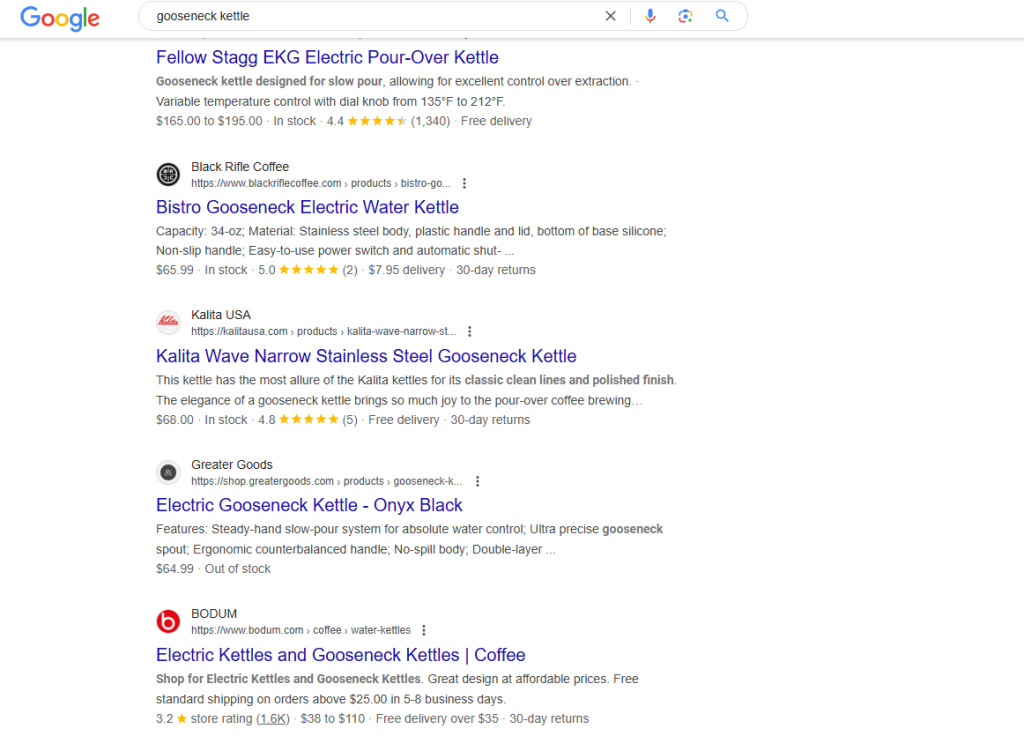
Find your direct competitors by googling your primary product terms. For Fellow Products, let’s search “gooseneck kettle” or “pour over coffee maker” in Google.
The brands appearing consistently in top positions are your SEO competitors. Aside from Fellow, we see Kalita and Bodum:
Analyze their rankings.
Analyze their domains using Ahrefs, SEMrush, Moz or any other SEO research tool.
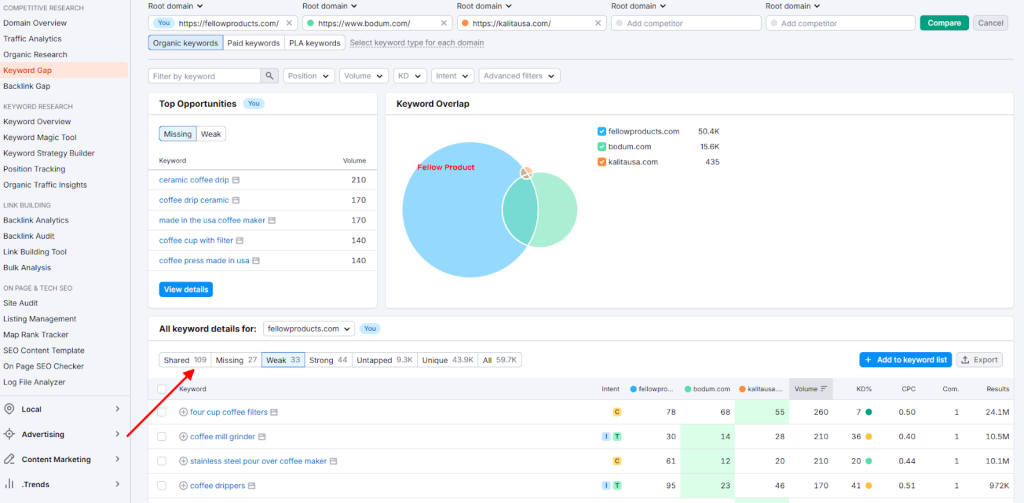
Here, you can see that although Fellow Products (in blue) has a larger share of all keywords, there are still some weak and missing keywords that they’re not ranking for. They can optimize for these keywords to compete more with Bodum and Kalita.
In your analysis, you can look for high-traffic product pages, keywords with commercial intent, competitor pages ranking in positions 1-3 and keywords with medium difficulty scores (say, 40-70, depending on your domain authority).
For example, for our client, if a competitor ranks well for “glass pour over coffee maker” while we’re not ranking at all, it’s an opportunity to optimize our glass product lines for similar keywords to be more visible on the results page.
Study their top-performing pages:
For each competitor keyword, you want to see their ranking page structure, keyword placement, and the product features they emphasize. You probably want to review their internal linking patterns too.
All these help you create new product and category pages for those keyword gaps to improve your ranking potential on the results page.
You can also create long-form blog content around the keywords driving competitor traffic. If the keyword is strategic and has commercial intent, it can attract relevant clicks from search results.
3. Optimize Your Title Tags
Now, let’s talk on-page SEO:
On-page SEO involves optimizing the blog, product and category pages to rank higher on SERPs. For e-commerce SEO and websites, this means making your pages appealing to search engines and shoppers ready to buy.
Google uses these on-page elements to understand what you’re selling and who should see it in search results. Get these elements right, and you’ll see higher rankings and more sales.
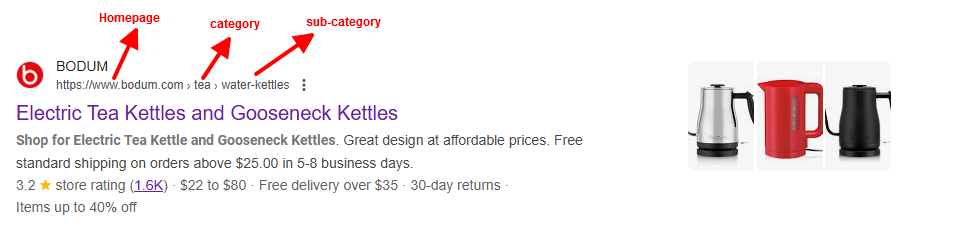
This visibility starts with your title tag, the clickable headline in search results. They need to be specific and compelling, like this:
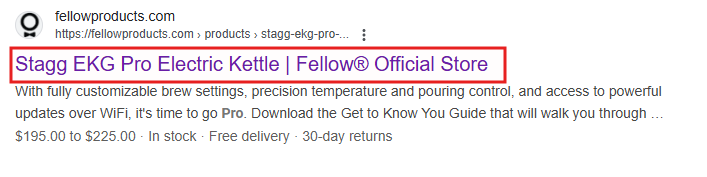
A poor example would have been “Coffee Kettle | Fellow Official Store”.
It’s not specific, so always write the product name, key specifications, and your brand name and keep everything between 55-60 characters.
Then, write a meta description that can attract clicks. Your meta description is your 155-character sales pitch in the search results. While not a direct ranking factor, it affects whether people click through to your site.
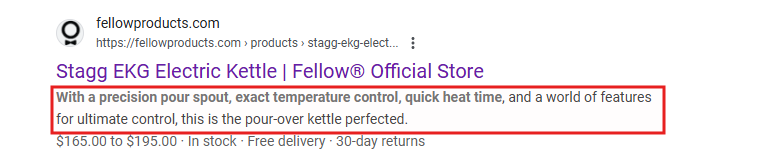
While writing yours, highlight key features, use schema markup to include pricing, star rating, and other information a shopper would like to know, and use your primary keyword naturally.
More on schema markup in point number six.
4. Use Search-Engine Friendly URLs
You’ll notice URL strings immediately if you search for anything on Google. That’s because they display a company’s brand name to attract the user’s attention. Especially if you remember that company.
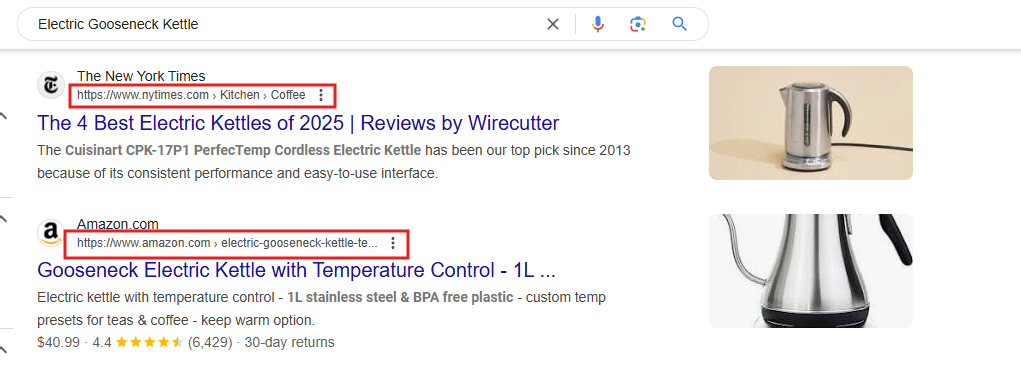
Your URL structure has a high chance of increasing click-through rates (CTR) and helping you rank higher online. This is because it includes your primary keyword and product name. And that’s why it must be clear and descriptive to help search engines understand your pages and increase users’ likelihood of clicking.
So, for e-commerce SEO, structure your different types of URLs like this:
- Category pages: /category-name/.
- Subcategory pages: /category-name/subcategory/.
- Product pages: /category-name/subcategory/product-name/.
Example for a pet store: mydomain.com/pet-supplies/cat-food/organic-salmon-dry-food/.
Bad: mydomain.com/products?id=4592&cat=14&type=food.
The latter isn’t specific and may affect the ranking potential of that page. Because it simply won’t rank for the keywords you optimized it for.
So, check some of your pages that aren’t performing right now to see if you have made this mistake while publishing it.
5. Optimize Your Product Pages with Relevant Keywords
Product and category pages serve different purposes in your e-commerce SEO strategy.
A product page focuses on a specific item and provides detailed information to help users make a purchase decision. A category page groups related products together to help users browse and compare options.
Your product pages should focus on converting visitors who are ready to buy. The most effective product pages include:
Write a detailed product description
A detailed product description (300-500 words) that addresses key buying criteria:
- Essential features and specifications.
- Key benefits that solve customer problems.
- Product variants (size, color, etc. when demand exists).
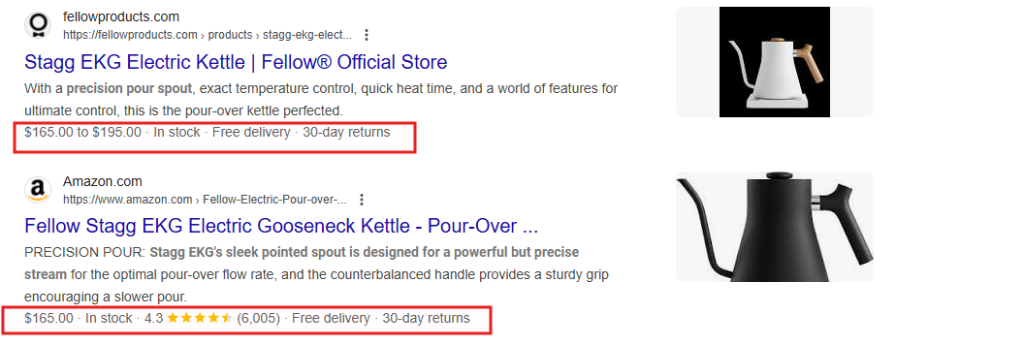
Here’s an example from Fellow’s electric kettle:
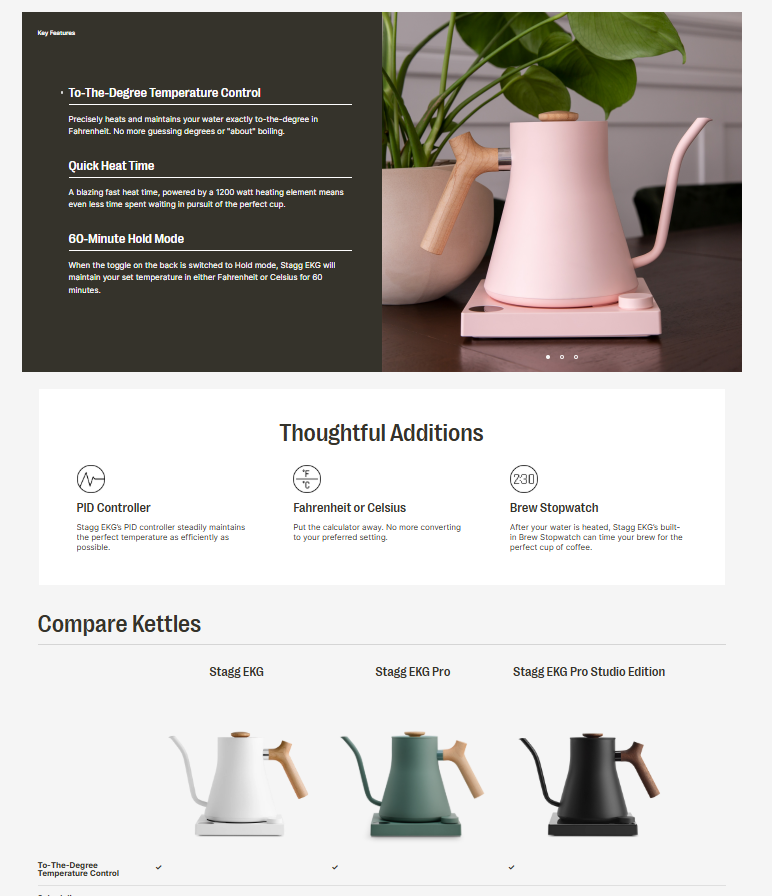
Add customer reviews and ratings when you have them.
But avoid empty review sections—only display reviews once you have 10+ verified customer ratings. This builds credibility through social proof.
Here’s an example of an e-commerce brand in the pet food industry doing that:
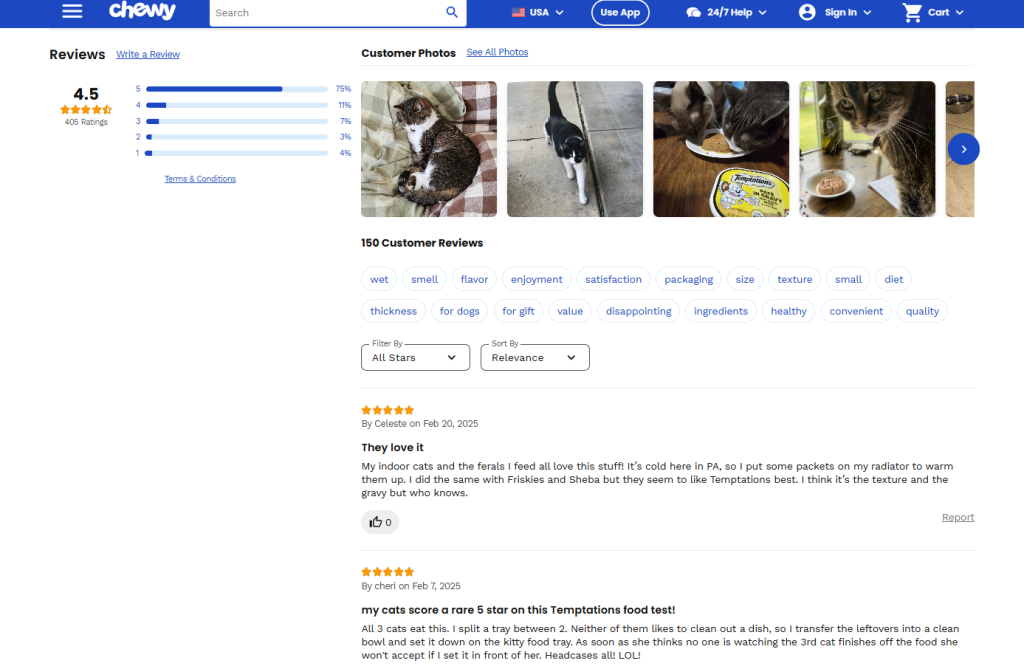
If you open this link, you’ll see high-quality pictures of their food pack, feeding instructions, nutritional information, and other important details a shopper wants to know.
Do the same thing, and your product pages will convert faster.
Use high-quality images
High-quality images showing the product from multiple angles. These images should load quickly and include descriptive alt text for SEO value.
That’s why the best e-commerce brands use a mix of pictures and videos:
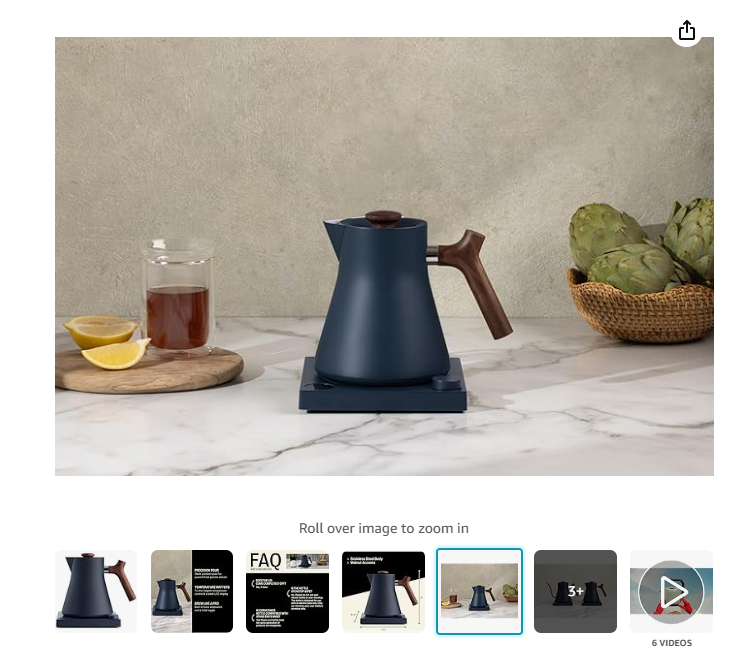
6. Use Rich Snippets and Schema Markup
Rich snippets improve how your products appear in search results. Instead of basic titles and descriptions, they show important product information like prices, availability, and star ratings directly in search results.
Schema markup is the code you add to your website’s HTML that makes this happen. It helps search engines understand your content better and provides context about what your content means rather than just what it says.
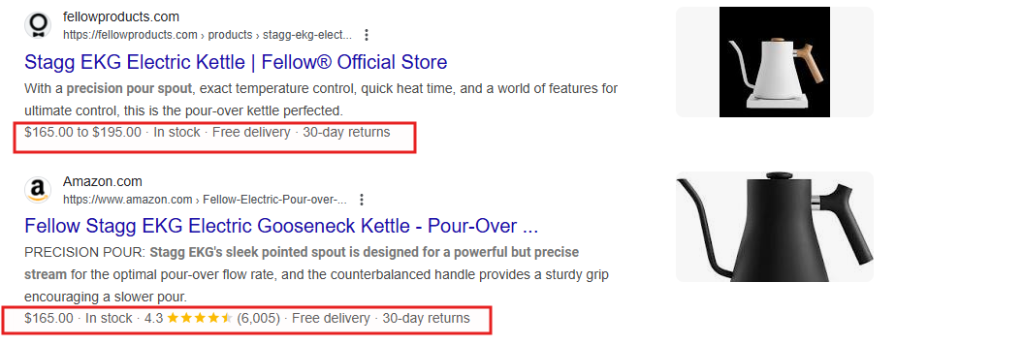
This additional context helps your listings stand out and attract more qualified clicks.
Here’s a real example of product schema in your code:
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org/”,
“@type”: “Product”,
“name”: “Professional Coffee Grinder”,
“description”: “Commercial-grade burr grinder for precise coffee grinding”,
“image”: “https://example.com/grinder-image.jpg”,
“brand”: {
“@type”: “Brand”,
“name”: “BrandName”
},
“offers”: {
“@type”: “Offer”,
“price”: “299.99”,
“priceCurrency”: “USD”,
“availability”: “https://schema.org/InStock”
},
“aggregateRating”: {
“@type”: “AggregateRating”,
“ratingValue”: “4.8”,
“reviewCount”: “47”
}
}
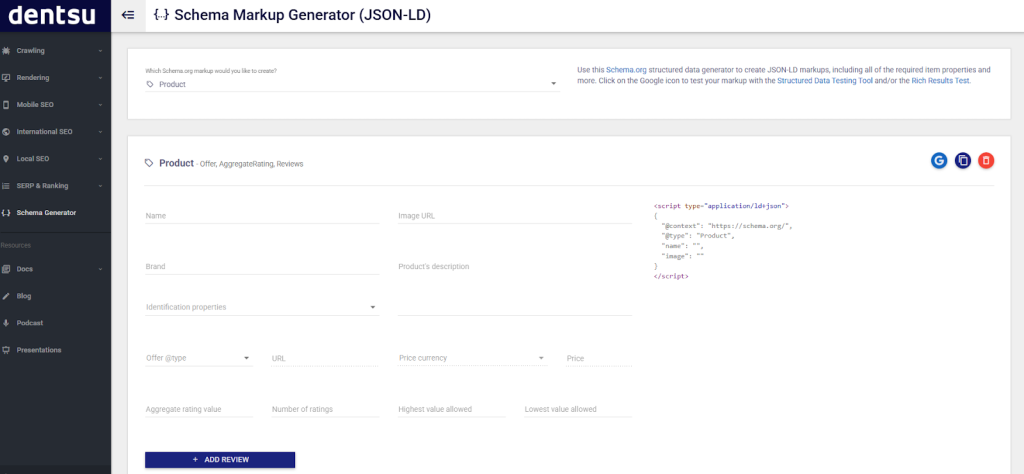
You don’t need to write your code manually tho. You can use different markup generator tools to create one for your e-commerce website (e.g. dentsu). All you need to do is fill out the requested details for the type of schema markup you need and it’ll auto-generate the code for you:
Note: Always double-check your code before pasting it in your HTML. You can do that using Google’s Rich Result Test. Here’s a result from the code I created earlier:
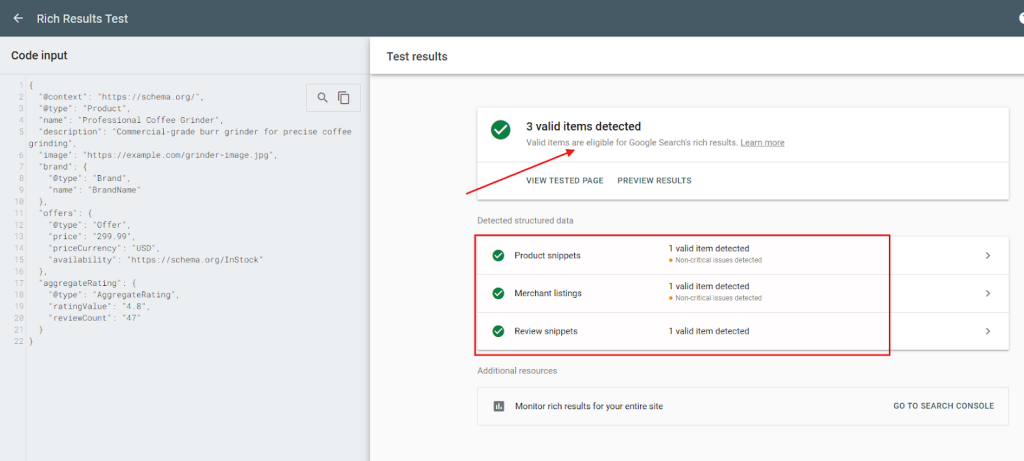
If I had not checked, I wouldn’t have been able to address the three issues Google picked.
Finally, only include Schema markup for elements that actually exist on your page. For example, don’t add review markup if you don’t have customer reviews.
7. Internal links
Internal linking does more than connect your pages—it shapes how Google understands and ranks your store. Take a look at this:
And look at this:
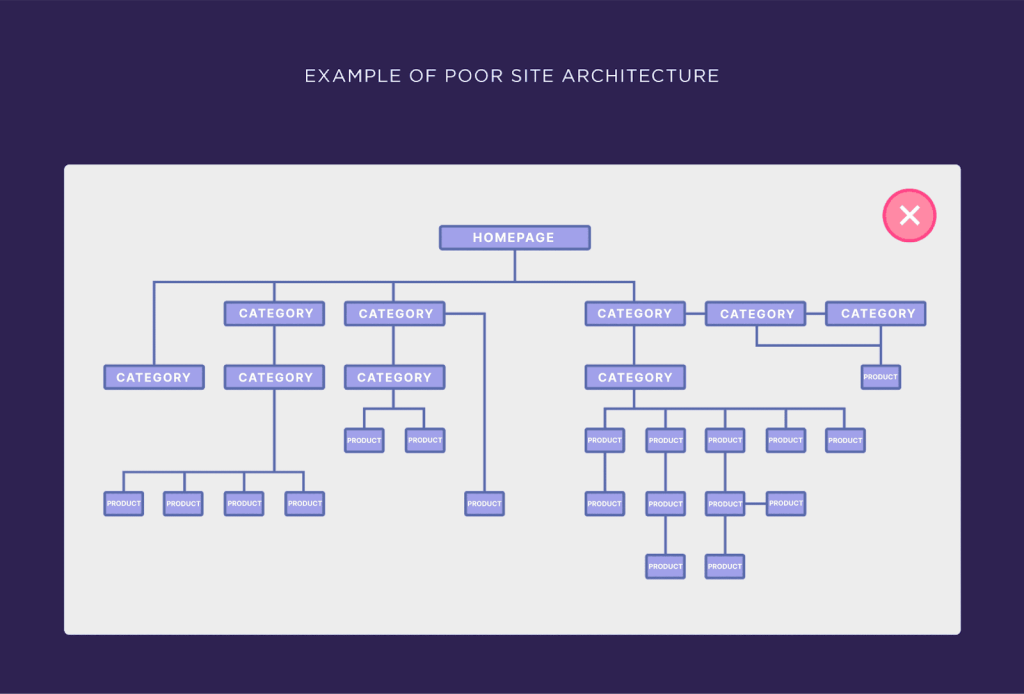
Which one looks navigable?
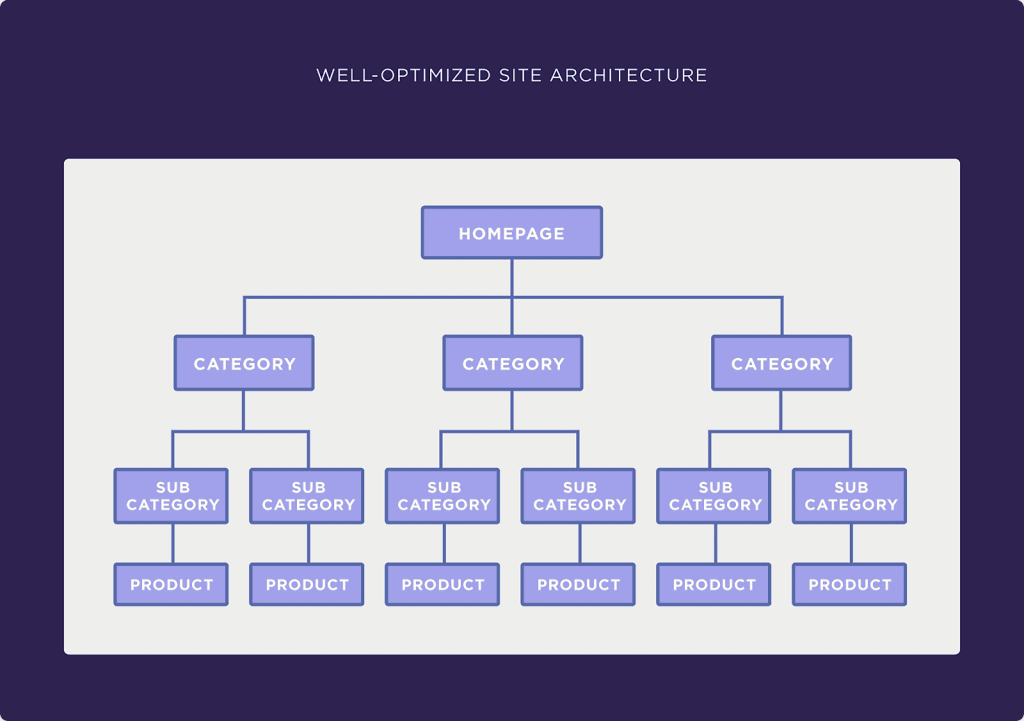
Well, I’d go for the first one— and that’s because the website architecture is built in a logical way that links the category to the subcategory which is then linked to the product. All these links are also connected to the homepage, perfect! Here’s what that looks like:
Unlike the second structure, where the product categories are scattered, there are even categories under categories. This structure will confuse Google bots and make your website complex to index, making your product and category pages hard to find.
In other words, your e-commerce site’s internal linking should follow a logical hierarchy.
You’ll need to hire a developer or technical SEO specialist to check if your website architecture is perfect and well-connected.
With that out of the way, always send more internal links to priority pages. These are pages with best-selling products, high-margin items, new releases or products with strong conversion rates. Here’s what chewy.com did here:
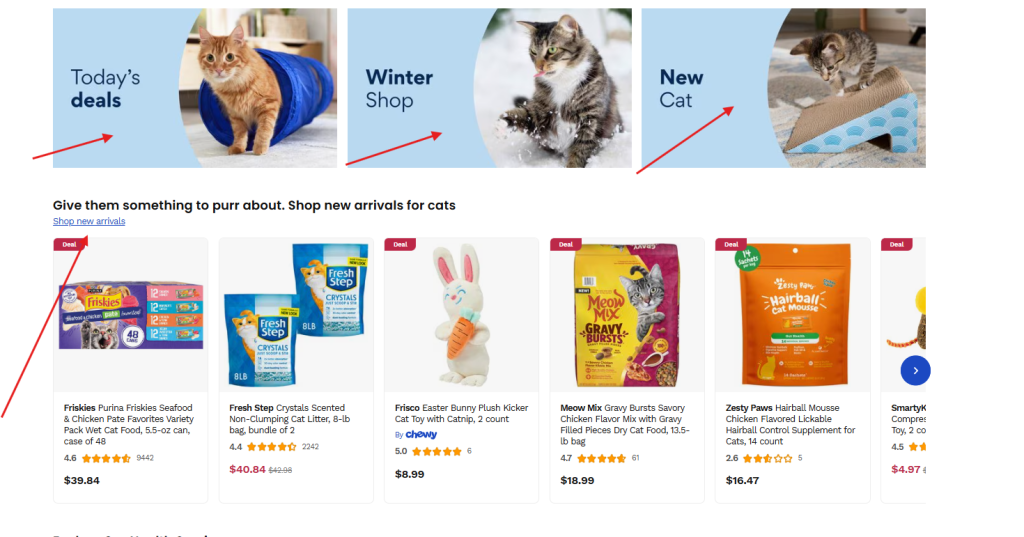
These links aren’t supposed to be on this page, but they are because they add more value to the page.
You can also do this by featuring best-sellers on your homepage or category pages. You can even add a “Staff Picks” or “Most Popular” section like Fellow Products did here:
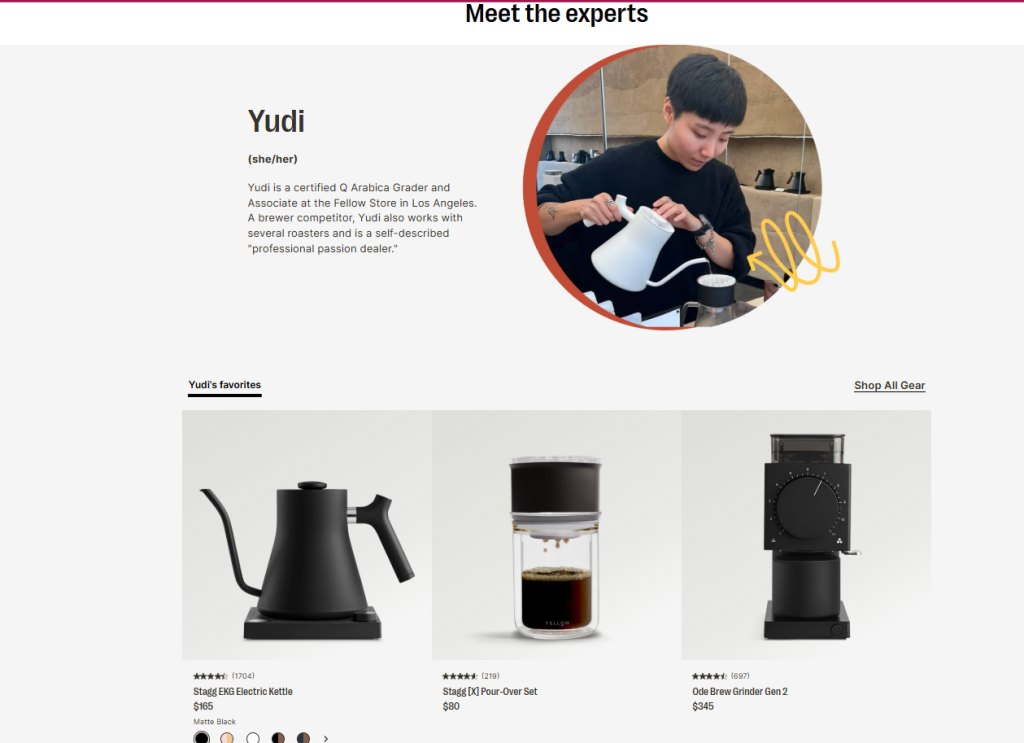
8. User Experience (UX)
Google heavily emphasizes user experience through its Page Experience signals.
A great user experience helps convert searchers into buyers and keeps them coming back. Here’s what matters most when it comes to user experience:
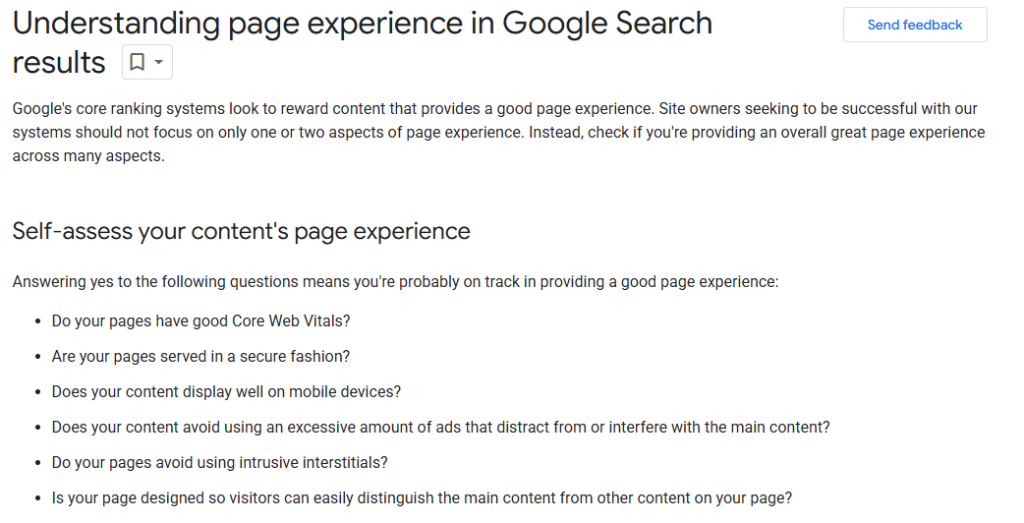
A. Core Web Vitals
Google measures three key aspects of user experience:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures how fast your largest content loads for the user .
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Measures your web page responsiveness to user inputs like taps and clicks.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures your page’s stability: elements on your page should stay stable as content loads.
These metrics directly impact your search rankings and conversion rates. The slower your website loads, the bad for your website because those users won’t keep waiting around; they’ll exit your page.
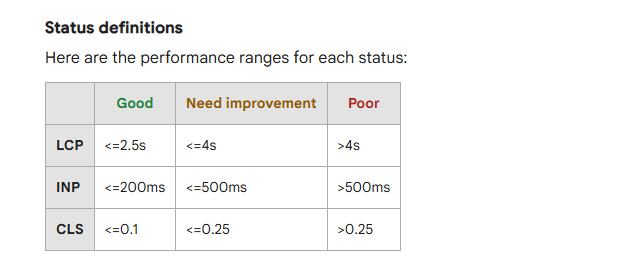
Use PageSpeedInsights to track your core web vitals and page speed. Here’s the benchmark every website must meet, according to Google:
Here’s a report for Fellow Products.
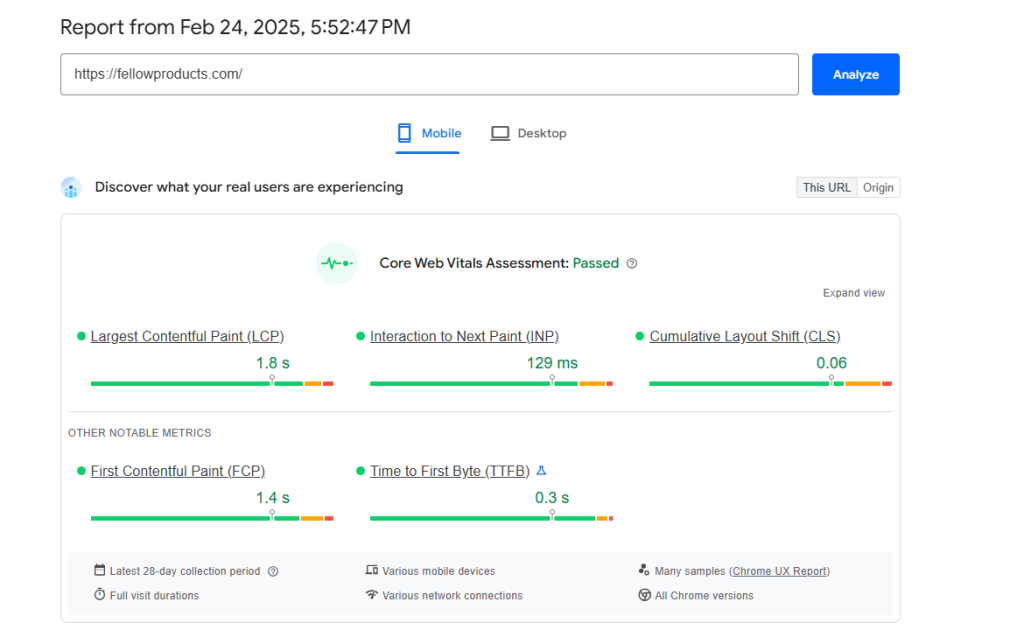
As you can see, it’s all green. This is what your e-commerce website should look like too.
B. Navigation Structure
Make your website easily navigable. This helps users easily browse through your pages, see your product offerings, and take any actions they want to take.
You can create a clear path to purchase by doing these:
- Limit menu options to prevent choice paralysis.
- Place products no more than 3 clicks from your homepage.
- Use clear category labels that match search terms. .
- Include a prominent search bar with filters.
- Display recently viewed items.
C. Product Discovery
Help shoppers find products quickly by doing these:
- Add filtering options (price, size, color, etc).
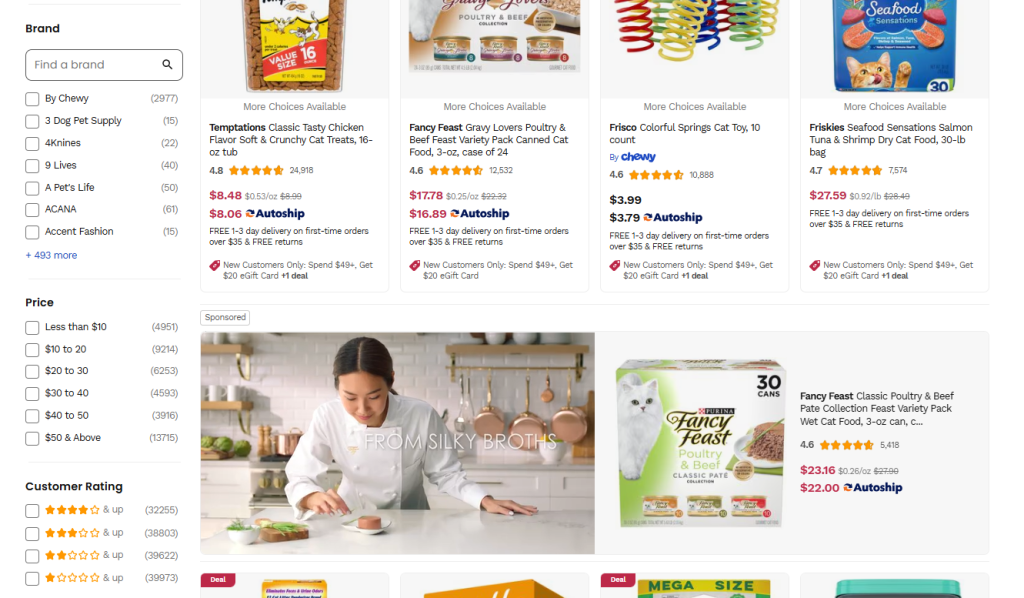
- Include high-quality product images from multiple angles.
- Show related products and “customers also bought” suggestions.
- Allow predictive search with common misspellings.
- Use product categories that match how people shop.
All these can improve your e-commerce blog’s user experience and increase overall sales.
9. Mobile Optimization
Over three-quarters of smartphone traffic in the US is e-commerce traffic. This means that mobile SEO is important, and there’s a flaw in your e-commerce SEO strategy if your website isn’t optimized to convert mobile traffic.
To optimize your site for mobile traffic:
- Use a responsive design that adapts to all screen sizes.
- Ensure text is readable without zooming.
- Make buttons and links large enough to tap easily.
- Test your site across multiple devices and browsers.
Mobile performance is also important, so website speed matters. If necessary, compress your images without compromising quality, implement lazy loading for images, minimize JavaScript and CSS files, and use a content delivery network (CDN) to speed up webpage loading.
Read more about mobile SEO here.
Conclusion
SEO is a huge factor in e-commerce success.
Ranking your website and product pages on the first page will help you secure more organic traffic. Beyond that, it helps you build brand awareness, which is a significant factor for customer loyalty.
Instead of paying for ads to drive traffic and sales, you can do it organically through SEO. We understand if you can’t DIY this, especially if you need to focus on inventory, delivery management, and other things that help your business operations. You can partner with a company with a proven history of success—check our e-commerce SEO service to see how we can help.
